


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 8-5-2021
Date: 5-5-2021
Date: 29-4-2021
|
Common-gate circuit
The common-gate circuit (Fig. 1) has the gate at signal ground. The input is applied to the source. The illustration shows an N-channel JFET. For other types of FETs, the same considerations apply as described above for the common-source circuit. Enhancement-mode devices would require a resistor between the gate and the positive supply terminal (or the negative terminal if the MOSFET is P-channel).
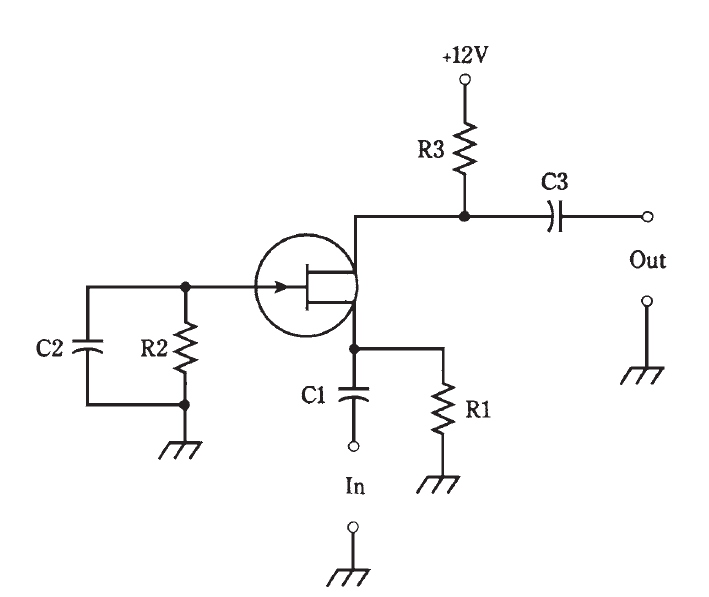
Fig. 1: Common-gate circuit configuration.
The dc bias for the common-gate circuit is basically the same as that for the common- source arrangement. But the signal follows a different path. The ac input signal enters through C1. Resistor R1 keeps the input from being shorted to ground. Gate bias is provided by R1 and R2; capacitor C2 places the gate at signal ground. In some common- gate circuits, the gate electrode is directly grounded, and components R2 and C2 are not used. The output leaves the circuit through C3. Resistor R3 keeps the output signal from being shorted through the power supply.
The common-gate arrangement produces less gain than its common-source counterpart. But this is not all bad; a common-gate amplifier is very stable, and is not likely to break into unwanted oscillation. The output is in phase with the input.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|