


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 22-4-2021
Date: 25-4-2021
Date: 22-4-2021
|
Voltage amplification
The graph of Fig. 1 shows the drain (channel) current, ID, as a function of the gate bias voltage, EG, for a hypothetical N-channel JFET. The drain voltage, ED, is assumed to be constant.
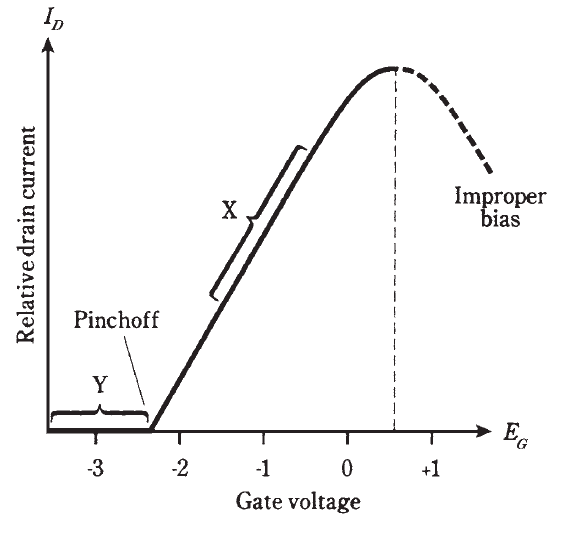
Fig. 1 Relative drain current as a function of gate voltage for a hypothetical N-channel JFET.
When EG is fairly large and negative, the JFET is pinched off, and no current flows through the channel. As EG gets less negative, the channel opens up, and current begins flowing. As EG gets still less negative, the channel gets wider and the current ID increases. As EG approaches the point where the SG junction is at forward breakover, the channel conducts as well as it possibly can.
If EG becomes positive enough so that the SG junction conducts, the JFET will no longer work properly. Some of the current in the channel will then be shunted off through the gate, a situation that is never desired in a JFET. The hose will spring a leak!
The best amplification for weak signals is obtained when the gate bias, EG, is such that the slope of the curve in Fig. 1 is the greatest. This is shown roughly by the range marked X in the figure. For power amplification, however, results are often best when the JFET is biased at, or even beyond, pinchoff, in the range marked Y.
The current ID passes through the drain resistor. Small fluctuations in EG cause large changes in ID, and these variations in turn produce wide swings in the dc voltage across R3 (at A) or R4 (at B). The ac part of this voltage goes through capacitor C2, and appears at the output as a signal of much greater ac voltage than that of the input signal at the gate. That’s voltage amplification.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مدرسة دار العلم.. صرح علميّ متميز في كربلاء لنشر علوم أهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|