


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 29-3-2021
Date: 3-5-2021
Date: 12-5-2021
|
The volt
You learned a little about the volt, the standard unit of electromotive force (EMF) or potential difference.
An accumulation of static electric charge, such as an excess or shortage of electrons, is always, associated with a voltage. There are other situations in which voltages exist. Voltage is generated at a power plant, and produced in an electrochemical reaction, and caused by light falling on a special semiconductor chip. It can be produced when an object is moved in a magnetic field, or is placed in a fluctuating magnetic field. A potential difference between two points produces an electric field, represented by electric lines of flux (Fig.1). There is always a pole that is relatively positive, with fewer electrons, and one that is relatively negative, with more electrons. The positive pole does not necessarily have a deficiency of electrons compared with neutral objects, and the negative pole might not actually have a surplus of electrons with respect to neutral things. But there’s always a difference in charge between the two poles. The negative pole always has more electrons than the positive pole.
The abbreviation for volt is V. Sometimes, smaller units are used. The millivolt (mV) is equal to a thousandth (0.001) of a volt. The microvolt (μV) is equal to a millionth (0.000001) of a volt. And it is sometimes necessary to use units much larger than one volt. One kilovolt (kV) is equal to one thousand volts (1,000). One megavolt (MV) is equal to one million volts (1,000,000) or one thousand kilovolts. In a dry cell, the EMF is usually between 1.2 and 1.7 V; in a car battery, it is most
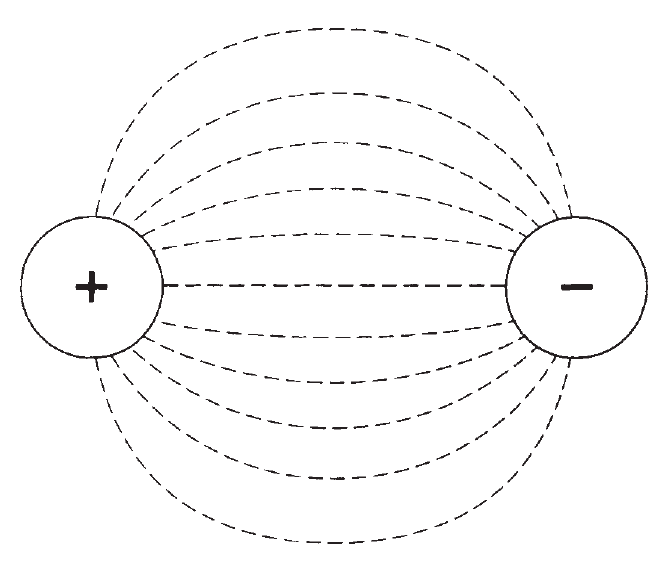
Fig.1: Electric lines of flux always exist near poles of electric charge.
often 12 V to 14 V. In household utility wiring, it is a low-frequency alternating current of about 117 V for electric lights and most appliances, and 234 V for a washing machine, dryer, oven, or stove. In television sets, transformers convert 117 V to around 450 V for the operation of the picture tube. In some broadcast transmitters, kilovolts are used. The largest voltages on Earth occur between clouds, or between clouds and the ground, in thundershowers; this potential difference is on the order of tens of megavolts.
In every case, voltage, EMF, or potential difference represents the fact that charge carriers will flow between two points if a conductive path is provided. The number of charge carriers might be small even if the voltage is huge, or very large even if the voltage is tiny. Voltage represents the pressure or driving force that impels the charge carriers to move. In general, for a given number of charge carriers, higher voltages will produce a faster flow, and therefore a larger current. It’s something like water pressure. The amount of water that will flow through a hose is proportional to the water pressure, all other things being equal.



|
|
|
|
علامات تحذيرية قد تسبق الموت القلبي المفاجئ لدى الشباب
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
استنساخ ذئاب عملاقة وشرسة "انقرضت منذ آلاف السنين"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أصواتٌ قرآنية واعدة .. أكثر من 80 برعماً يشارك في المحفل القرآني الرمضاني بالصحن الحيدري الشريف
|
|
|