


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 22-5-2016
Date: 27-3-2021
Date: 28-3-2021
|
STATISTICAL MECHANICS OF BOSONS AND FERMIONS
The most general system of noninteracting particles will have a variety of single particle energy eigenstates, labeled by a parameter p, which can be discrete or continuous and range over a finite or infinite number of values. The space of p values might also have a geometrical structure corresponding to some number of spatial dimensions. As an example, p could label both the three vector momentum P and the J3 component of the spin σ of a nonrelativistic particle of any spin j. The momentum would be discrete if space were a torus, and would live on a torus, the first Brillouin zone, if space were a lattice. Denote the energy of the p-th single particle state by ∈p.
The N-particle states are labeled by N copies of the quantum number p1, . . . pN, which are either symmetric or totally antisymmetric under permutations of the copies. The key to statistical mechanics is the realization that a nonredundant labeling of the states is just to give the number of particles n(p) occupying each single particle state p. For bosons, n(p) can be any nonnegative integer, while for fermions, it is either zero or one. For either type of statistics, we have
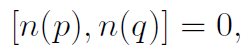
which means that the Hilbert space breaks up into a tensor product H = ⊗ pHp, where n(p) acts as 1 ⊗ . . . n(p) ⊗ 1 . . . ⊗ 1. That is, n(p) acts in a nontrivial way only on the factor Hp.
Furthermore, because p is a full set of single particle quantum numbers, the states in Hp are completely characterized by the eigenvalue of n(p). For fermions, Hp is two dimensional, while for bosons, it is infinite dimensional.
In nonrelativistic physics, the numbers of each type of stable elementary particle (electrons, protons, neutrons inside nuclei which do not undergo beta decay) are conserved quantum numbers. From a relativistic perspective, this is because we never consider transitions between energy levels differing by more than about 10−4 of the electron mass. For the purposes of this chapter, we will consider only a single type of elementary particle, so that there is only one such conserved quantum number
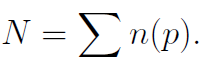
Conservation means that [N,H] = 0, which is evident from




|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تستعد لإطلاق الحفل المركزي لتخرج طلبة الجامعات العراقية
|
|
|