


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 2-1-2021
Date: 10-11-2020
Date: 8-1-2021
|
Blackbody Radiation
When electromagnetic radiation in an isothermal enclosure, or cavity, is in thermal equilibrium at temperature T , the distribution of radiation density  dν, contained in a bandwidth dν, is given by Planck’s law
dν, contained in a bandwidth dν, is given by Planck’s law
 ......(1)
......(1)
where  is the radiation density per unit frequency [J s/cm3], k is Boltzmann’s constant, and c is the velocity of light. The spectral distribution of thermal radiation vanishes at ν = 0 and ν → ∞, and has a peak which depends on the temperature.
is the radiation density per unit frequency [J s/cm3], k is Boltzmann’s constant, and c is the velocity of light. The spectral distribution of thermal radiation vanishes at ν = 0 and ν → ∞, and has a peak which depends on the temperature.
The factor
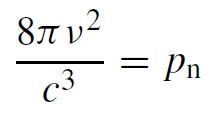 ......(2)
......(2)
in (1) gives the density of radiation modes per unit volume and unit frequency interval. The factor pn can also be interpreted as the number of degrees of freedom associated with a radiation field, per unit volume, per unit frequency interval. The expression for the mode density pn [modes s/cm3] plays an important role in connecting the spontaneous and the induced transition probabilities.
For a uniform, isotropic radiation field, the following relationship is valid
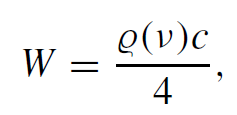 ..........(3)
..........(3)
where W is the blackbody radiation [W/cm2] which will be emitted from an opening in the cavity of the blackbody. Many solids radiate like a blackbody. Therefore, the radiation emitted from the surface of a solid can be calculated from (3).
According to the Stefan–Boltzmann equation, the total blackbody radiation is
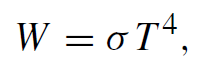 .......(4)
.......(4)
where σ = 5.68 × 10−12 W/cm2 K4. The emitted radiation W has a maximum which is obtained from Wien’s displacement law
 ........(5)
........(5)
For example, a blackbody at a temperature of 5200 K has its radiation peak at 5564 A° , which is about the center of the visible spectrum.



|
|
|
|
"إنقاص الوزن".. مشروب تقليدي قد يتفوق على حقن "أوزيمبيك"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الصين تحقق اختراقا بطائرة مسيرة مزودة بالذكاء الاصطناعي
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ووفد من جامعة البصرة يبحثان سبل تعزيز التعاون المشترك
|
|
|