


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 8-9-2020
Date: 25-8-2020
Date: 27-8-2020
|
Measuring distance in the Solar System: The Moon
The Moon is the only natural object in the Solar System whose distance can be found accurately using the classical parallax method.
In principle, it involves the simultaneous measurement of the meridian zenith distance of the Moon at two observatories with the same longitude but widely separated in latitude. The wide latitude separation provides a reasonably long base-line Let observatories O1 and O2 have latitudes ∅1 N and ∅2 S. Let the meridian zenith distances of the Moon be z10 and z20 at these two observatories, that is Z10 = ∠Z1O1M and Z20 = ∠Z2O2M (see figure 1).
Then if z1 and z2 are the true (i.e. geocentric) zenith distances for observatories O1 and O2 respectively, with p1 and p2 the parallactic angles O1MC and O2MC, we may write
∅1 + ∅2 = z1 + z2 (1)
z1 = z10 − p1 z2 = z20 − p2 (2)
p1 = P sin z10 p2 = P sin z20 (3)
where P is the value of the Moon’s horizontal parallax when the observations are made.
By equations (3),
P = (p1 + p2)/(sin z10 + sin z20).
By equations (2),
p1 + p2 = z10 + z20 − (z1 + z2).
By equation (1), then, we have
P = [z10 + z20 − (∅1 + ∅2)]/(sin z10 + sin z20) (4)
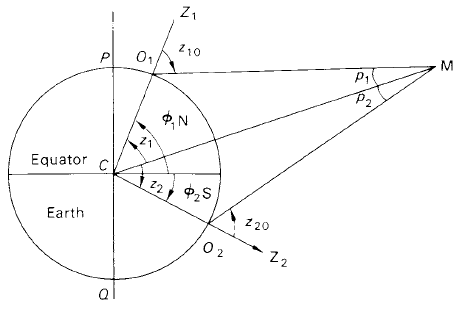
Figure 1. Measurement of the Moon’s distance by observations from two sites.
so that P may be calculated from known and measured quantities. Knowing the radius of the Earth.
In practice, the procedure is complicated by a number of factors. The observatories are never quite on the same meridian of longitude so that a correction has to be made for the change in the Moon’s declination in the time interval between its transits across the two observatories’ respective meridians. In addition, theMoon is not a point source of light. Agreement, therefore, has to be made between the observatories as to which crater to observe, a correction thereafter giving the distance between the centres of Earth and Moon.
Due allowance must be made for the individual instrumental errors and the local values of refraction. In the case of the Moon, its parallax is so large that any residual error is not great. Since the advent of radar, laser methods and lunar probes, including lunar artificial satellites, the Moon’s distance can be measured very accurately. The limiting accuracy is partly due to the accuracy with which the velocity of light is known but also involves the accuracy with which the Earth observing stations’ geodetic positions are known. Uncertainties are of the order of 0·1 of a metre, the average
distance being 384 400 kilometres.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|