


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 8-3-2019
Date: 22-3-2017
Date: 2-2-2018
|
As we begin our summary of periodic trends, recall that the single most important unifying principle in understanding the chemistry of the elements is the systematic increase in atomic number, accompanied by the orderly filling of atomic orbitals by electrons, which leads to periodicity in such properties as atomic and ionic size, ionization energy, electronegativity, and electron affinity. The same factors also lead to periodicity in valence electron configurations, which for each group results in similarities in oxidation states and the formation of compounds with common stoichiometries.
The most important periodic trends in atomic properties are summarized in Figure .1 . Recall that these trends are based on periodic variations in a single fundamental property, the effective nuclear charge (Zeff), which increases from left to right and from top to bottom in the periodic table.
The diagonal line in Figure .1 separates the metals (to the left of the line) from the nonmetals (to the right of the line). Because metals have relatively low electronegativities, they tend to lose electrons in chemical reactions to elements that have relatively high electronegativities, forming compounds in which they have positive oxidation states. Conversely, nonmetals have high electronegativities, and they therefore tend to gain electrons in chemical reactions to form compounds in which they have negative oxidation states. The semimetals lie along the diagonal line dividing metals and nonmetals. It is not surprising that they tend to exhibit properties and reactivities intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. Because the elements of groups 13, 14, and 15 span the diagonal line separating metals and nonmetals, their chemistry is more complex than predicted based solely on their valence electron configurations.
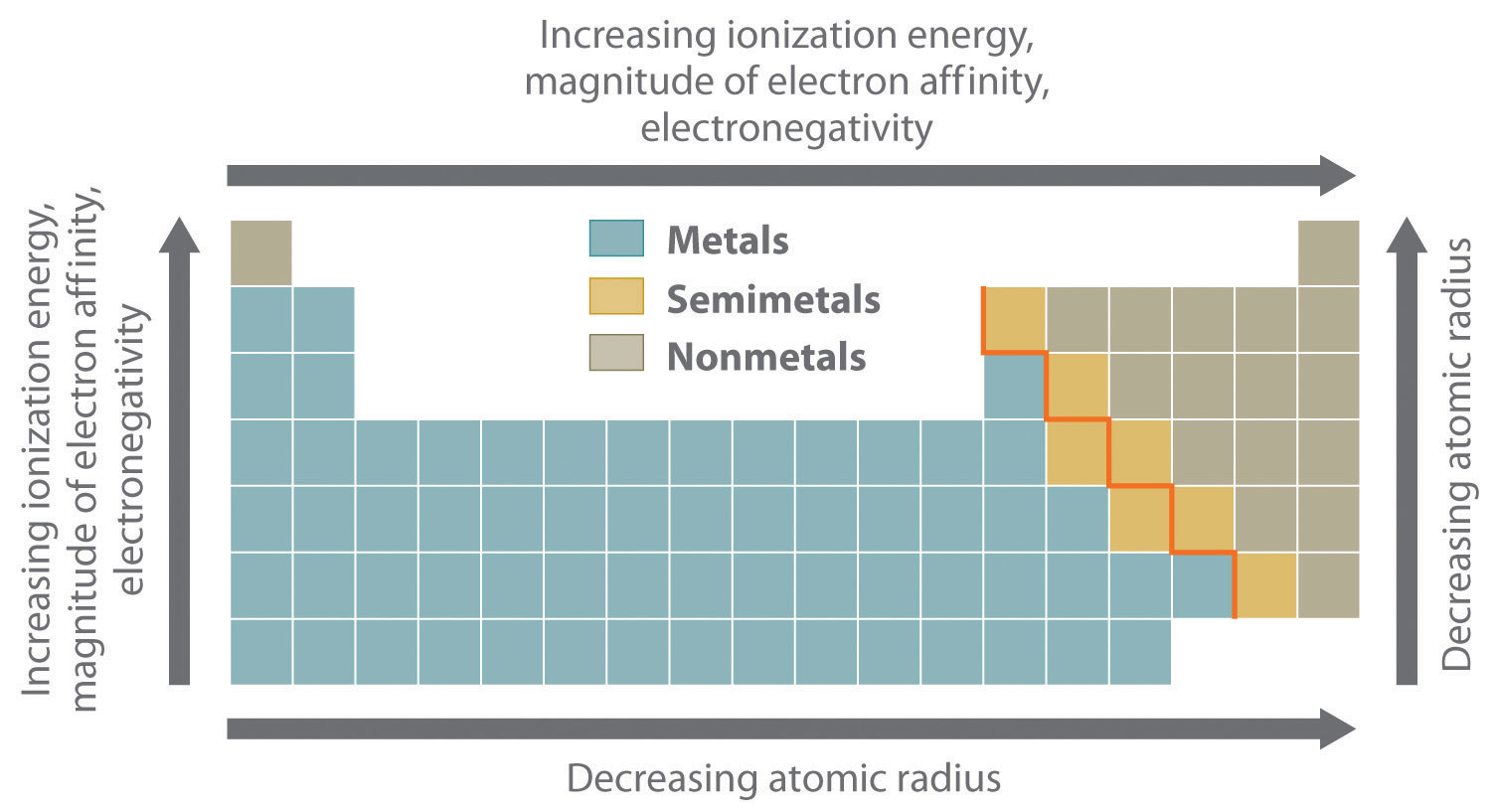
Figure .1 : Summary of Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties. Ionization energies, the magnitude of electron affinities, and electronegativities generally increase from left to right and from bottom to top. In contrast, atomic size decreases from left to right and from bottom to top. Consequently, the elements in the upper right of the periodic table are the smallest and most electronegative; the elements in the bottom left are the largest and least electronegative. The semimetals lie along the diagonal line separating the metals from the nonmetals and exhibit intermediate properties.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
سماحة السيد الصافي يؤكد ضرورة تعريف المجتمعات بأهمية مبادئ أهل البيت (عليهم السلام) في إيجاد حلول للمشاكل الاجتماعية
|
|
|