


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 17-3-2020
Date: 25-2-2020
Date: 5-3-2020
|
When an X-ray is shined on a crystal, it diffracts in a pattern characteristic of the structure. In powder X-ray diffraction, the diffraction pattern is obtained from a powder of the material, rather than an individual crystal. Powder diffraction is often easier and more convenient than single crystal diffraction since it does not require individual crystals be made. Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) also obtains a diffraction pattern for the bulk material of a crystalline solid, rather than of a single crystal, which doesn't necessarily represent the overall material. A diffraction pattern plots intensity against the angle of the detector, 2θ
Since most materials have unique diffraction patterns, compounds can be identified by using a database of diffraction patterns. The purity of a sample can also be determined from its diffraction pattern, as well as the composition of any impurities present. A diffraction pattern can also be used to determine and refine the lattice parameters of a crystal structure. A theoretical structure can also be refined using a method known as Rietveld refinement. The particle size of the powder can also be determined by using the Scherrer formula, which relates the particle size to the peak width. The Scherrer fomula is
with
· BM is the observed peak width,
· BS is the peak width of a crystalline standard, and
· θ is the angle of diffraction.
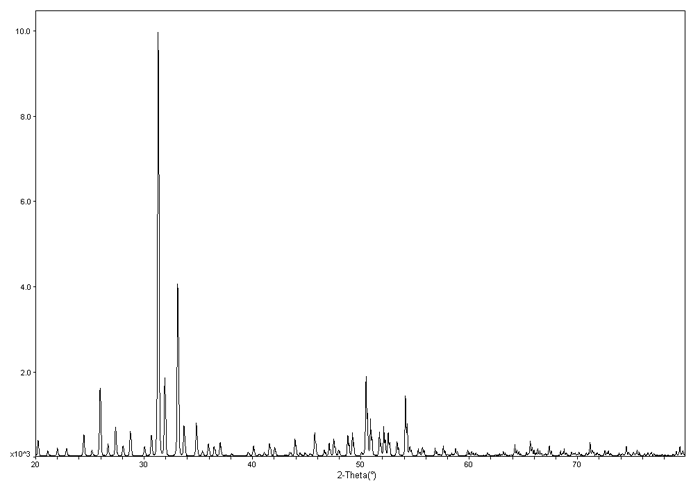
To the left is an example XRD pattern for Ba24Ge100
. The x axis is 2θ and the y axis is the intensity.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|