


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 27-8-2018
Date: 27-12-2019
Date: 24-8-2018
|
Nucleotides are joined together through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the OH group on the third carbon atom of the sugar unit of a second nucleotide. This unit joins to a third nucleotide, and the process is repeated to produce a long nucleic acid chain (Figure 1). The backbone of the chain consists of alternating phosphate and sugar units (2-deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA). The purine and pyrimidine bases branch off this backbone.
Each phosphate group has one acidic hydrogen atom that is ionized at physiological pH. This is why these compounds are known as nucleic acids.
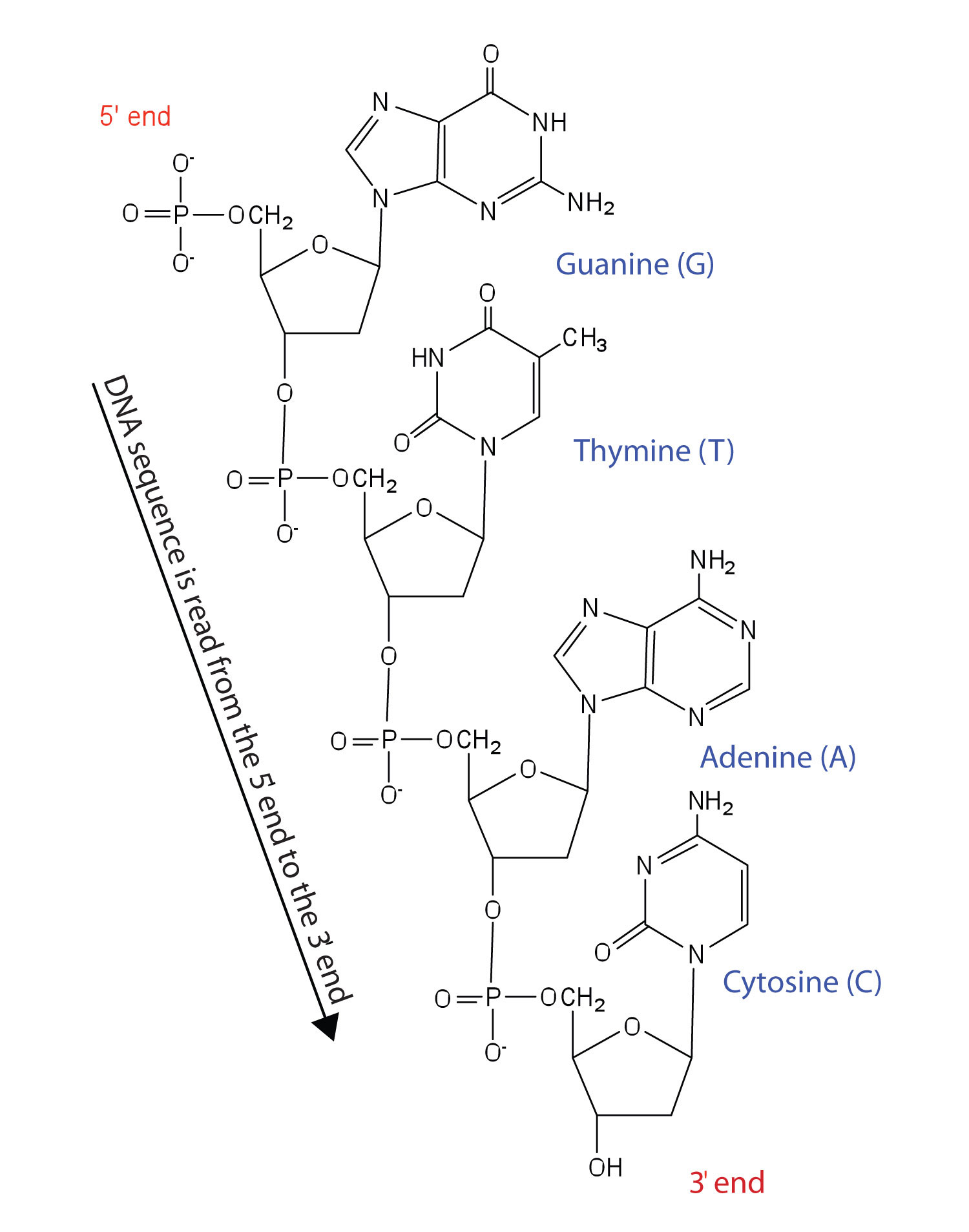
Figure 1 Structure of a Segment of DNA. A similar segment of RNA would have OH groups on each C2′, and uracil would replace thymine.
Like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides. Unlike proteins, which have 20 different kinds of amino acids, there are only 4 different kinds of nucleotides in nucleic acids. For amino acid sequences in proteins, the convention is to write the amino acids in order starting with the N-terminal amino acid. In writing nucleotide sequences for nucleic acids, the convention is to write the nucleotides (usually using the one-letter abbreviations for the bases, shown in Figure 1) starting with the nucleotide having a free phosphate group, which is known as the 5′ end, and indicate the nucleotides in order. For DNA, a lowercase d is often written in front of the sequence to indicate that the monomers are deoxyribonucleotides. The final nucleotide has a free OH group on the 3′ carbon atom and is called the 3′ end. The sequence of nucleotides in the DNA segment shown in Figure 1 would be written 5′-dG-dT-dA-dC-3′, which is often further abbreviated to dGTAC or just GTAC.![]()



|
|
|
|
دراسة: حفنة من الجوز يوميا تحميك من سرطان القولون
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تنشيط أول مفاعل ملح منصهر يستعمل الثوريوم في العالم.. سباق "الأرنب والسلحفاة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تطلق فعاليات الاحتفاء بموسوعة مؤلفات الإماميّة
|
|
|