


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 2-9-2018
Date: 2-11-2020
Date: 26-5-2019
|
Just as an atom is the simplest unit that has the fundamental chemical properties of an element, a molecule is the simplest unit that has the fundamental chemical properties of a covalent compound. Some pure elements exist as covalent molecules. Hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and the halogens occur naturally as the diatomic (“two atoms”) molecules H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, and I2 (part (a) in Figure 1.1). Similarly, a few pure elements exist as polyatomic (“many atoms”) molecules, such as elemental phosphorus and sulfur, which occur as P4 and S8 (part (b) in Figure 1.1 ).
Each covalent compound is represented by a molecular formula, which gives the atomic symbol for each component element, in a prescribed order, accompanied by a subscript indicating the number of atoms of that element in the molecule. The subscript is written only if the number of atoms is greater than 1. For example, water, with two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom per molecule, is written as H2O . Similarly, carbon dioxide, which contains one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms in each molecule, is written as CO2.
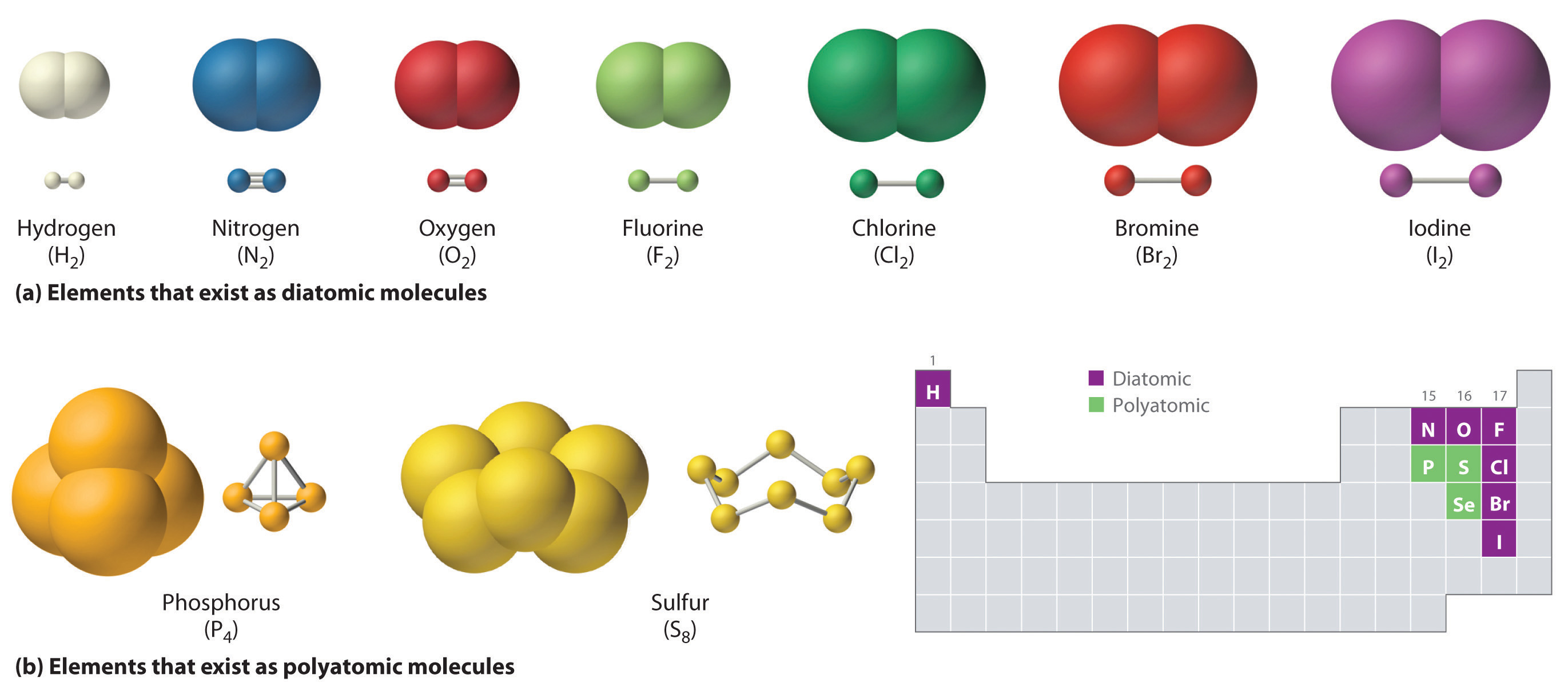
Figure 1.1 : Elements That Exist as Covalent Molecules. (a) Several elements naturally exist as diatomic molecules, in which two atoms (E) are joined by one or more covalent bonds to form a molecule with the general formula E2. (b) A few elements naturally exist as polyatomic molecules, which contain more than two atoms. For example, phosphorus exists as P4 tetrahedra—regular polyhedra with four triangular sides—with a phosphorus atom at each vertex. Elemental sulfur consists of a puckered ring of eight sulfur atoms connected by single bonds. Selenium is not shown due to the complexity of its structure.
Covalent compounds that predominantly contain carbon and hydrogen are called organic compounds. The convention for representing the formulas of organic compounds is to write carbon first, followed by hydrogen and then any other elements in alphabetical order (e.g., CH4O is methyl alcohol, a fuel). Compounds that consist primarily of elements other than carbon and hydrogen are called inorganic compounds; they include both covalent and ionic compounds. In inorganic compounds, the component elements are listed beginning with the one farthest to the left in the periodic table, as in CO2 or SF6. Those in the same group are listed beginning with the lower element and working up, as in ClF. By convention, however, when an inorganic compound contains both hydrogen and an element from groups 13–15, hydrogen is usually listed last in the formula. Examples are ammonia (NH3) and silane (SiH4). Compounds such as water, whose compositions were established long before this convention was adopted, are always written with hydrogen first: Water is always written as H2O, not OH2.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي ينظّم ندوة حوارية حول مفهوم العولمة الرقمية في بابل
|
|
|