


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 1-4-2019
Date: 31-12-2018
Date: 25-11-2018
|
The usual source of vanadium in the +5 oxidation state is ammonium metavanadate, NH4VO3. This isn't very soluble in water and is usually first dissolved in sodium hydroxide solution. The solution can be reduced using zinc and an acid - either hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid, usually using moderately concentrated acid. The exact vanadium ion present in the solution is very complicated, and varies with the pH of the solution. The reaction is done under acidic conditions when the main ion present is VO2+ - called the dioxovanadium(V) ion.
If you do the reaction in a small flask, it is normally stoppered with some cotton wool. This allows hydrogen (produced from a side reaction between the zinc and acid) to escape. At the same time it stops much air from entering. This prevents re-oxidation of the lower oxidation states of vanadium (particularly the +2 state) by oxygen in the air. The reaction is usually warmed so that the changes happen in a reasonable time. The reduction is shown in two stages. Some individual important colors are shown, but the process is one continuous change from start to finish.
The reduction from +5 to +4

It is important to notice that the green color you see isn't actually another oxidation state. it is just a mixture of the original yellow of the +5 state and the blue of the +4. Be very careful with the formulae of the two vanadium ions - they are very easy to confuse!
The reduction from +4 to +2. The color changes just continue.
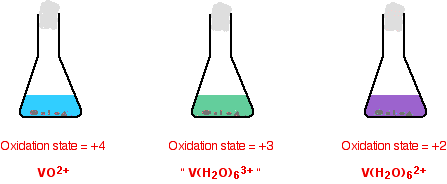
The reason for the inverted commas around the vanadium(III) ion is that this is almost certainly a simplification. The exact nature of the complex ion will depend on which acid you use in the reduction process. The simplification is probably reasonable at this level.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مدرسة دار العلم.. صرح علميّ متميز في كربلاء لنشر علوم أهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|