
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Work-Energy Theorem
المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
الجزء والصفحة:
p 96
15-12-2016
2564
Work-Energy Theorem
Let's review what we have done. Work was defined as 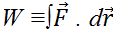 and by putting in F = ma we found that the total work is always ΔK where the kinetic energy is defined as
and by putting in F = ma we found that the total work is always ΔK where the kinetic energy is defined as 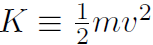 . Thus
. Thus
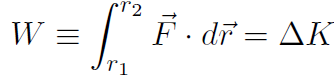
So far so good. Note carefully what we did to get this result. We put in the right hand side of F = ma to prove W = ΔK. What we actually did was

Now let's not put 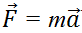 but just study the integral
but just study the integral 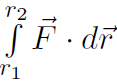 by itself. Before we do that, we must recognize that there are two types of forces called conservative and non-conservative. Anyway, to put it briefly, conservative forces ''bounce back" and non-conservative forces don't. Gravity is a conservative force. If you lift an object against gravity and let it go then the object falls back to where it was. Spring forces are conservative. If you pull a spring and then let it go, it bounces back to where it was. However friction is non-conservative. If you slide an object along the table against friction and let go, then the object just stays there. With conservative forces we always associate a potential energy. Thus any force
by itself. Before we do that, we must recognize that there are two types of forces called conservative and non-conservative. Anyway, to put it briefly, conservative forces ''bounce back" and non-conservative forces don't. Gravity is a conservative force. If you lift an object against gravity and let it go then the object falls back to where it was. Spring forces are conservative. If you pull a spring and then let it go, it bounces back to where it was. However friction is non-conservative. If you slide an object along the table against friction and let go, then the object just stays there. With conservative forces we always associate a potential energy. Thus any force  can be broken up into the conservative piece
can be broken up into the conservative piece  C and the non-conservative piece
C and the non-conservative piece  NC, as in
NC, as in
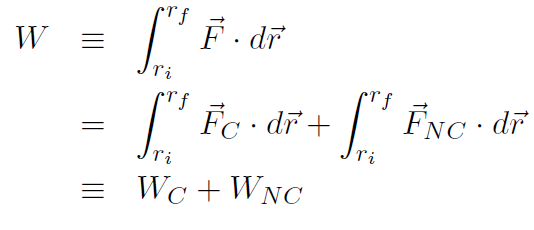
and each piece corresponds therefore to conservative work WC and non-conservative work WNC. Let's define the conservative piece as the negative of the change in a new quantity called potential energy U. The definition is
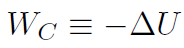
where -ΔU = -(Uf - Ui) = -Uf + Ui. Now we found that the total work W was always ΔK. Combining all of this we have

or
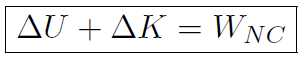
which is the famous Work-Energy theorem.