
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Uniform Circular Motion
المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
الجزء والصفحة:
P 58
12-12-2016
2428
Uniform Circular Motion
In today's world of satellites and spacecraft circular motion is very important to understand because many satellites have circular orbits. Also circular motion is a classic example where we have a definite non-zero acceleration even though the speed of a satellite is constant. This occurs because the direction of velocity is constantly changing for the satellite even though the magnitude of velocity (i.e. speed) is constant. The word ''uniform" means that speed is constant. In circular motion, there is a well-defined radius which we will call r. Also the time it takes for the satellite to complete 1 orbit is called the period T. If the speed is constant then it is given by
 (1.1)
(1.1)
Here I have written  instead of
instead of 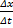 or
or  because Δs is the total distance around the circle which is a mixture of x and y.
because Δs is the total distance around the circle which is a mixture of x and y.  is just the distance of 1 orbit (circumference) divided by the time of 1 orbit (period). What about the acceleration? Well that's just a =
is just the distance of 1 orbit (circumference) divided by the time of 1 orbit (period). What about the acceleration? Well that's just a =  but how do we work it out? Look at Figure 1.1, where the displacement and velocity vectors are drawn for a satellite at two different positions P1 and P2.
but how do we work it out? Look at Figure 1.1, where the displacement and velocity vectors are drawn for a satellite at two different positions P1 and P2.
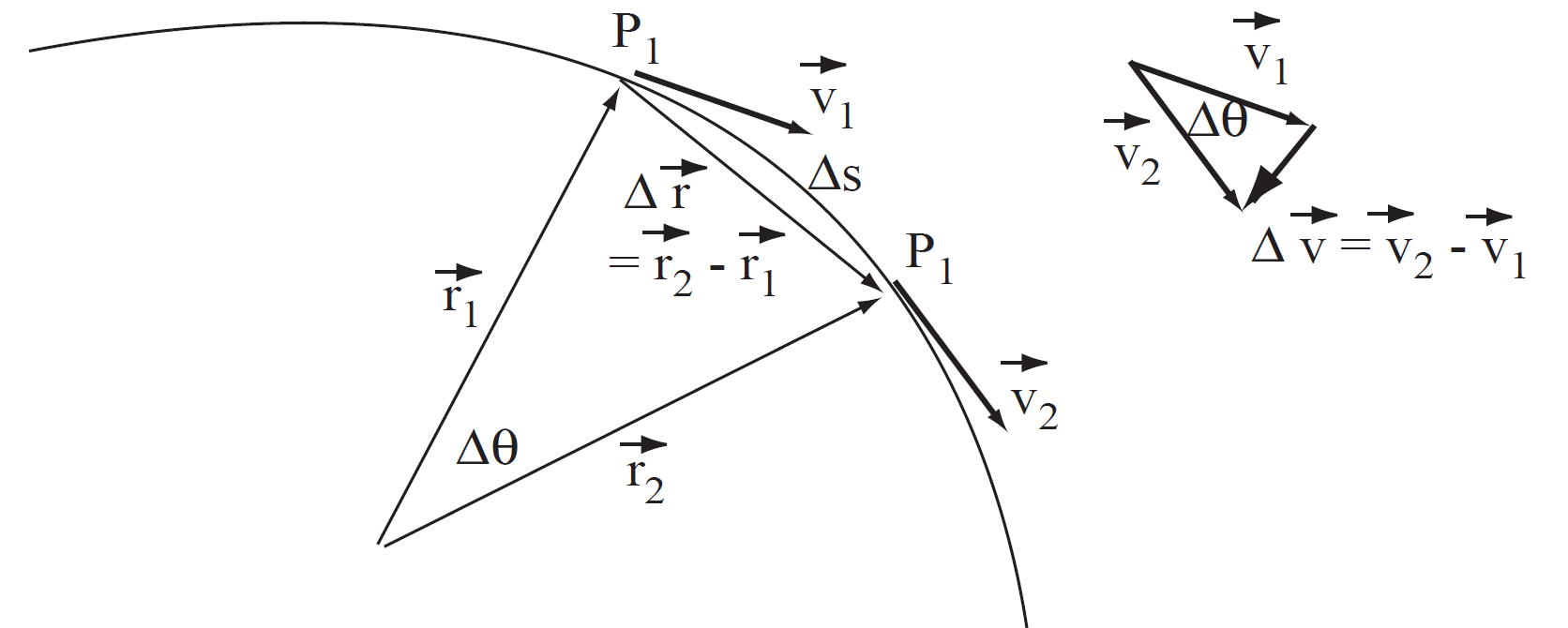
FIGURE 1.1 Circular Motion.
Now angle Δθ is defined as (with 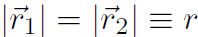 )
)
 (1.2)
(1.2)
The velocity vectors can be re-drawn as in the bottom part of the figure. The triangle is similar to the top triangle in that the angle Δθ is the same. Also the speed v is constant, meaning that
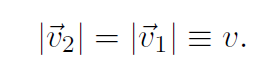 (1.3)
(1.3)
Writing 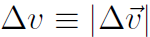 the bottom figure also gives
the bottom figure also gives
 (1.4)
(1.4)
Now the magnitude of acceleration is
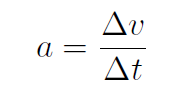 (1.5)
(1.5)
Combining the above two equations for Δθ gives  , i.e.
, i.e.
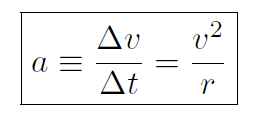 (1.6)
(1.6)
This is a very important equation. Whenever we have uniform circular motion we always know the actual value of acceleration if we know v and r. We have worked out the magnitude of the acceleration. What about its direction? I will show you a VIDEO in class which will clearly show that the direction of acceleration is always towards the center of the circle. For this reason it is called centripetal acceleration. One final thing. When you drive your car around in a circle then you, as the driver, feel as though you are getting pushed against the door. In reality it is the car that is being accelerated around in the circle, and because of your inertia, the car pushes on you. This ''acceleration" that you feel is the same as the car's acceleration. The ''acceleration" you feel is called the centrifugal acceleration. The same idea occurs when you spin-dry clothes in a washing machine.
Example Future spacecraft will be made to spin in order to provide artificial gravity for the astronauts. Suppose the spacecraft is a cylinder of L in length. Derive a formula for the rotation period would it need to spin in order to simulate the gravity on Earth. If L = 1 km what is the numerical value foe the period ?
Solution The centifugal acceleration is a and we want it to equal
g. Thus
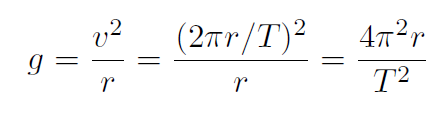
Thus
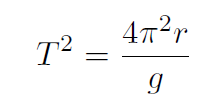
giving
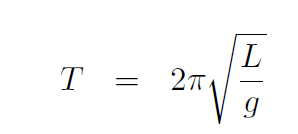
which is the formula we seek. Putting in numbers:
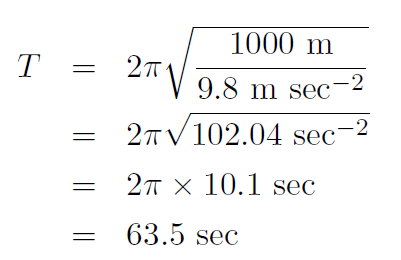
i.e. about once every minute!
Example The Moon is 1/4 million miles from Earth. How fast does the Moon travel in its orbit ?
Solution The period of the Moon is 1 month. Thus
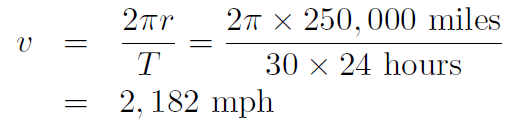
i.e. about 2000 mph!