


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 31-8-2017
Date: 24-7-2017
Date: 18-8-2017
|
DISPROPORTIONATION OF TOLUENE
The catalytic disproportionation of toluene (Figure 1.1) in the presence of hydrogen produces benzene and a xylene mixture. Disproportionation is an equilibrium reaction with a 58% conversion per pass theoretically possible. The reverse reaction is the transalkylation of xylenes with benzene:
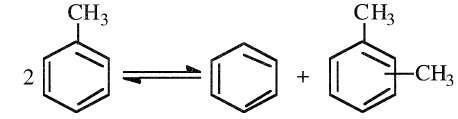
Typical conditions for the disproportionation reaction are 450–530°C and 20 atmospheres. A mixture of CoO-MoO3 on aluminosilicates/alumina catalysts can be used. Conversions of approximately 40% are normally used to avoid more side reactions and faster catalyst deactivation. The equilibrium constants for this reaction are not significantly changed by shifting from liquid to vapor phase or by large temperature changes.
Currently, zeolites, especially those of ZSM-5 type, are preferred for their higher activities and selectivities. They are also more stable thermally. Modifying ZSM-5 zeolites with phosphorous, boron, or magnesium compounds produces xylene mixtures rich in the p-isomer (70–90%). It has been proposed that the oxides of these elements, present in zeolites, reduce the dimensions of the pore openings and channels and so favor formation and outward diffusion of p-xylene, the isomer with the smallest minimum dimension.
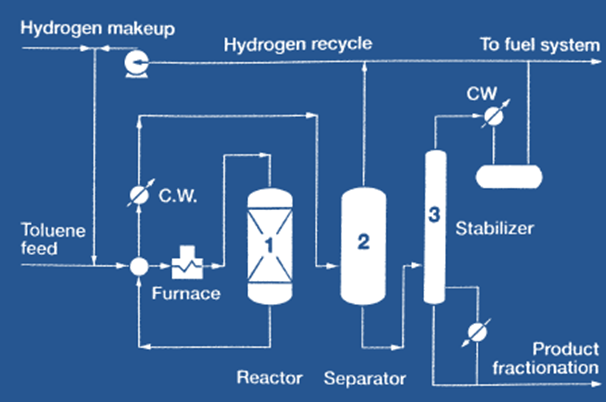
Figure 1.1. The Mobil Oil Corp., IFP process for the disproportionation of toluene to mixed xylenes.



|
|
|
|
دراسة: حفنة من الجوز يوميا تحميك من سرطان القولون
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تنشيط أول مفاعل ملح منصهر يستعمل الثوريوم في العالم.. سباق "الأرنب والسلحفاة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تكرّم الفائزين بمسابقة فنِّ الخطابة الثامنة
|
|
|