


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 21-8-2017
Date: 3-7-2019
Date: 31-7-2017
|
AMMOXIDATION OF PROPYLENE (Acrylonitrile [CH2=CHCN])
Ammoxidation refers to a reaction in which a methyl group with allyl hydrogens is converted to a nitrile group using ammonia and oxygen in the presence of a mixed oxides-based catalyst. A successful application of this reaction produces acrylonitrile from propylene:
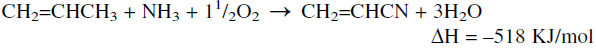
As with other oxidation reactions, ammoxidation of propylene is highly exothermic, so an efficient heat removal system is essential.
Acetonitrile and hydrogen cyanide are by-products that may be recovered for sale. Acetonitrile (CH3CN) is a high polarity aprotic solvent used in DNA synthesizers, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and electrochemistry. It is an important solvent for extracting butadiene from C4 streams. Table 8-1 shows the specifications of acrylonitrile, HCN, and acetonitrile.
Both fixed and fluid-bed reactors are used to produce acrylonitrile, but most modern processes use fluid-bed systems. The Montedison-UOP process (Figure 8-2) uses a highly active catalyst that gives 95.6% propylene conversion and a selectivity above 80% for acrylonitrile.
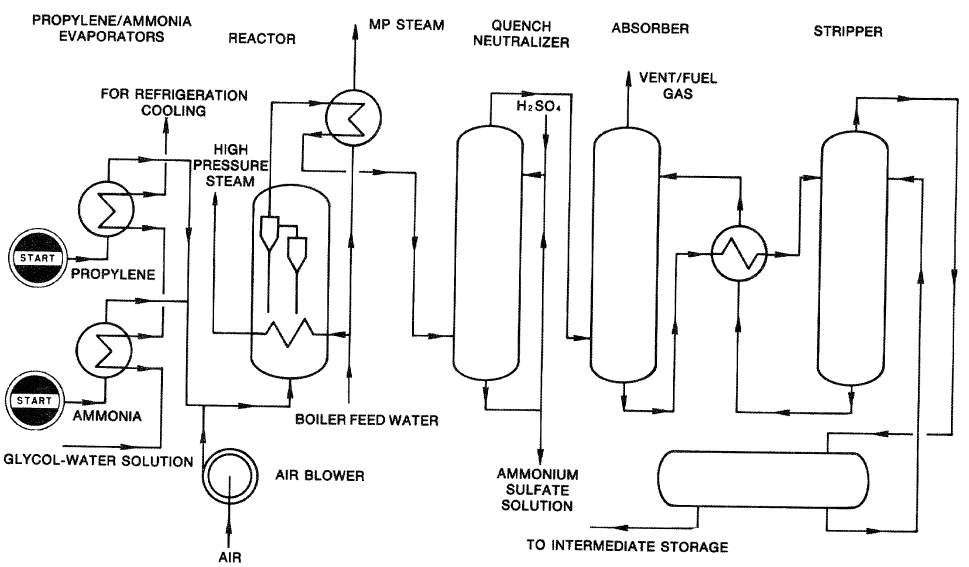
Figure 8-2. A flow diagram of the Montedison-UOP acrylonitrile process.
The catalysts used in ammoxidation are similar to those used in propylene oxidation to acrolein. Oxidation of propylene occurs readily at322°C over Bi-Mo catalysts.
Table 8-1 : Typical analysis of acrylonitrile, HCN and acetonitrile

However, in the presence of ammonia, the conversion of propylene to acrylonitrile does not occur until about 402°C. This may be due to the adsorption of ammonia on catalytic sites that block propylene chemisportion. As with propylene oxidation, the first step in the ammoxidation reaction is the abstraction of an alpha hydrogen from propylene and formation of an allylic intermediate.
Although the subsequent steps are not well established, it is believed that adsorbed ammonia dissociates on the catalyst surface by reacting with the lattice oxygen, producing water. The adsorbed NH species then reacts with a neighboring allylic intermediate to yield acrylonitrile.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|