


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 26-3-2017
Date: 27-4-2017
Date: 21-4-2017
|
Electron Capture (EC, K-capture)
Nuclei having an excess of protons may capture an electron from one of the inner orbits which immediately combines with a proton in the nucleus to form a neutron. This process is called electron capture (EC). The electron is normally captured from the innermost orbit (the K-shell), and, consequently, this process is sometimes called K-capture. The following example depicts electron capture.
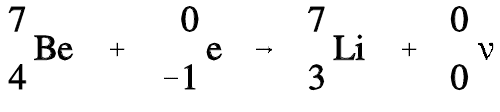
A neutrino is formed at the same time that the neutron is formed, and energy carried off by it serves to conserve momentum. Any energy that is available due to the atomic mass of the product being appreciably less than that of the parent will appear as gamma radiation. Also, there will always be characteristic x-rays given off when an electron from one of the higher energy shells moves in to fill the vacancy in the K-shell. Electron capture is shown graphically in Figure 1.
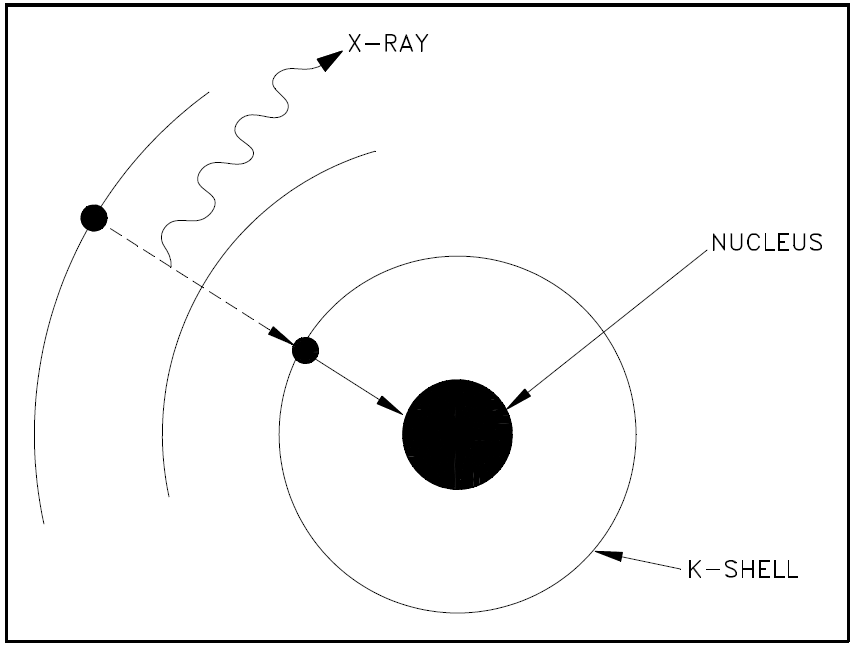
Figure1: Orbital Electron Capture
Electron capture and positron emission result in the production of the same daughter product, and they exist as competing processes.
For positron emission to occur, however, the mass of the daughter product must be less than the mass of the parent by an amount equal to at least twice the mass of an electron. This mass difference between the parent and daughter is necessary to account for two items present in the parent but not in the daughter. One item is the positron ejected from the nucleus of the parent. The other item is that the daughter product has one less orbital electron than the parent. If this requirement is not met, then orbital electron capture takes place exclusively.



|
|
|
|
لخفض ضغط الدم.. دراسة تحدد "تمارين مهمة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
بمناسبة مرور 40 يومًا على رحيله الهيأة العليا لإحياء التراث تعقد ندوة ثقافية لاستذكار العلامة المحقق السيد محمد رضا الجلالي
|
|
|