


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 29-9-2017
Date: 24-9-2017
Date: 5-10-2020
|
Initiator
Emulsion polymerization occurs almost entirely following the radical mechanism. The function of the initiator is to generate free radicals, which in turn lead to the propagation of the polymer molecules. The free radicals can be commonly produced by two main ways: (i) thermal decomposition, or (ii) redox reactions. In addition, the free-radical initiators can be either water or oil-soluble.
The most commonly used water-soluble initiators are persulfates (peroxodisulfates). For example, potassium-, sodium-, and ammonium-persulfate. Persulfate ion decomposes thermally in the aqueous phase to give two sulfate radical anions which can initiate the polymerization. Hydrogen peroxide and other peroxides are thermal decomposition type initiators and they are soluble in both the aqueous and monomer-swolen polymer phases. Besides of these, oil-soluble compounds such as benzoyl peroxide and azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) can be employed as thermal initiators in emulsion polymerizations. The other initiation system consists of redox initiators (such as persulfate-bisulfite system) which produce free radicals through an oxidation-reduction reaction at relatively low temperatures. The main types of free radicals which are produced by thermally or redox system are:
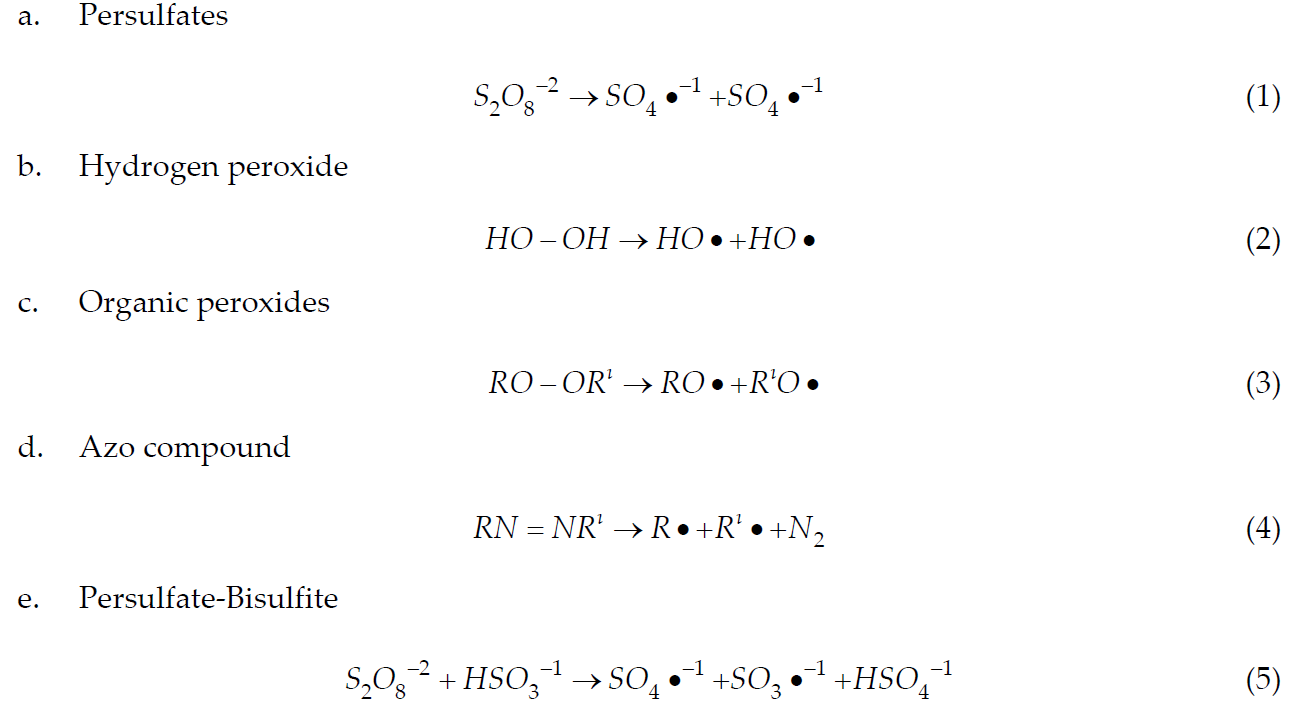
There is also surface active initiators which are called as “inisurfs”, for example; bis[2-(4'-sulfophenyl)alkyl]-2,2'-azodiisobutyrate ammonium salts and 2,2'-azobis(N-2'-methylpropanoyl-2-amino-alkyl-1-sulfonate)s. The initiators of this type carry stabilizing groups in their structures, and emulsion polymerization can be successfully carried out in the presence of them, without additional stabilizers up to more than 50% in solid content. Moreover, the free radicals needed to initiate the emulsion polymerization can be produced by ultrasonically, or radiation-induced. 60Co γ radiation is the most widely used as radiation-induced initiation system in the emulsion polymerizations.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتبة أمّ البنين النسويّة تصدر العدد 212 من مجلّة رياض الزهراء (عليها السلام)
|
|
|