
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Cylinder with Massive Piston
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 14
25-8-2016
1799
Cylinder with Massive Piston
Consider n moles of an ideal monatomic gas placed in a vertical cylinder. The top of the cylinder is closed by a piston of mass M and cross section A (see Figure 1.1). Initially the piston is fixed, and the gas has volume V0 and temperature T0. Next, the piston is released, and after several oscillations comes to a stop. Disregarding friction and the heat capacity of the piston and cylinder, find the temperature and volume of the gas at equilibrium. The system is thermally isolated, and the pressure outside the cylinder is Pa.
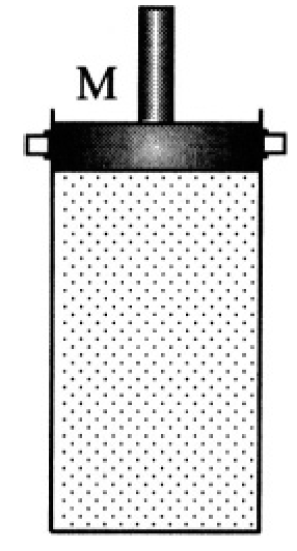
Figure 1.1
SOLUTION
When the piston is released, it will move in some, as yet unknown, direction. The gas will obey the ideal gas law at equilibrium, so
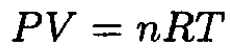 (1)
(1)
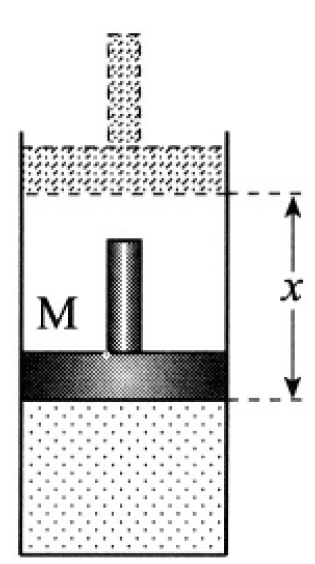
Figure 1.2
On the other hand, at equilibrium, there is no net force acting on the piston (see Figure 1.2), and we have
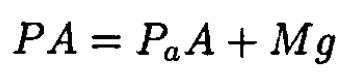 (2)
(2)
Substituting (2) into (1) gives
 (3)
(3)
We can also use energy conservation in this thermally insulated system. Then the work done to the gas equals its energy change ∆ε. For an ideal gas
 (4)
(4)
Where Cv is the heat capacity of one mole of the gas (for a monatomic gas, Cv = 3R/2). The work done to the gas
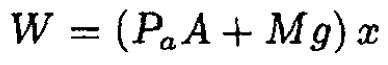 (5)
(5)
where x = (V0- V)/A is the distance the piston moves, where downward is positive. From (4) and (5), we have
 (6)
(6)
Solving (3) and (6) yields
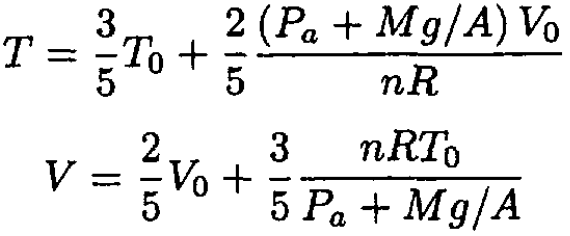 (7)
(7)
We may check that if P0 = Pa + Mg/A, i.e., that the piston was initially balanced, (7) gives T = T0 and V = V0.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















