


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 13-7-2016
Date: 19-8-2016
Date: 25-8-2016
|
Critical Field in Superconductor
Consider a massive cylinder of volume V made of a type I superconducting material in a magnetic field parallel to its axis.
a) Using the fact that the superconducting state displays perfect diamagnetism, whereas the normal state has negligible magnetic susceptibility, show that the entropy discontinuity across the phase boundary is at zero field H:
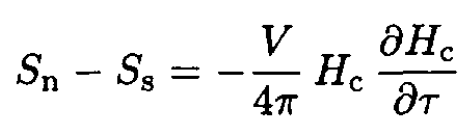
where Hc(τ) is the critical H field for suppressing superconductivity at a temperature τ.
b) What is the latent heat when the transition occurs in a field?
c) What is the specific heat discontinuity in zero field?
SOLUTION
a) If the external field is smaller than the critical field, H < HC, then the B-field inside the superconductor is zero, B = 0, and the magnetization M becomes
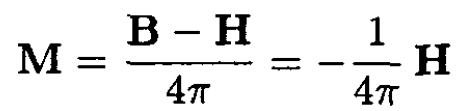 (1)
(1)
This means that the superconductor displays perfect diamagnetism (with magnetic susceptibility χ = -1/4π). The change in free energy of the
superconductor due to the increase of the external field H may be written as δF = -V . M . dH = (V/4π)H . dH. Therefore, the free energy of the superconductor in a field is given by
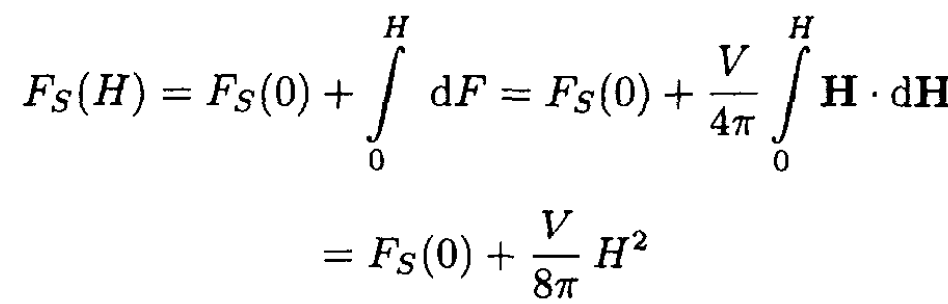 (2)
(2)
The transition to a normal state occurs when the free energy of the superconducting state is equal to that of the normal state:
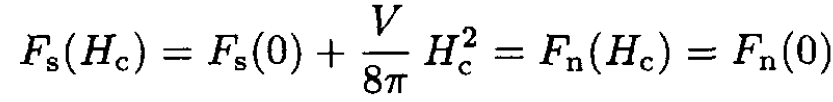 (3)
(3)
Here we used the fact that, because of the negligible magnetic susceptibility, the free energy of the normal state practically does not depend on the applied field. So, we have
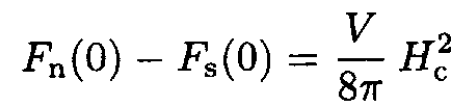 (4)
(4)
where HC ≡ HC(τ). Now, it is easy to calculate the entropy discontinuity since
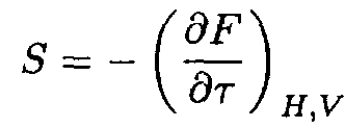 (5)
(5)
so
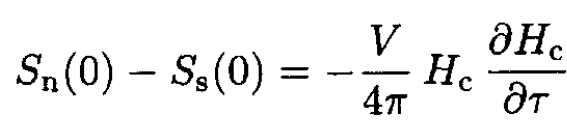 (6)
(6)
If we recall that the dependence of the critical field on the temperature can be approximated by the formula HC(τ) = H(0)[1 – t2], where t ≡ τ/τc then we can confirm that a superconducting state is a more ordered state, since ∂HC/∂τ < 0 and hence Sn > Ss.
b) The latent heat q, if the transition occurs at a constant temperature, is given by q = τ(Sn – Ss). If the transition is from superconducting to normal, then
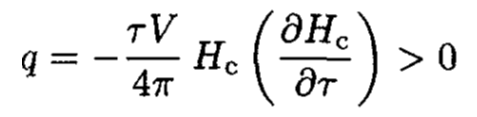 (7)
(7)
So, if we have a transition from the superconducting to normal states, then heat is absorbed.
c) The specific heat is defined as C = τ(∂S/∂τ). Here we disregard any volume and pressure changes due to the transition. Hence, from equation (6), the specific heat per volume discontinuity is
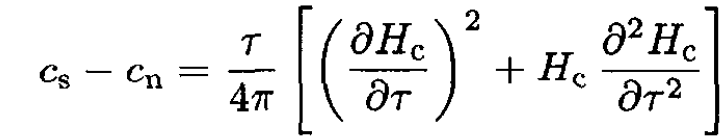 (8)
(8)
At zero field the transition is of second order and Hc(τc) = 0, so the specific heat per unit volume discontinuity at τ = τc from (8) is
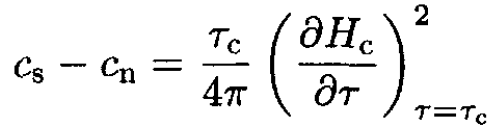 (9)
(9)



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|