
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء والفلسفة

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Atmospheric Energy
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 13
25-8-2016
1632
Atmospheric Energy
The density of the Earth’s atmosphere, ρ (z), varies with height z above the Earth’s surface. Assume that the “thickness” of the atmosphere is sufficiently small so that it is in a uniform gravitational field of strength g.
a) Write an equation to determine the atmospheric pressure P (z), given the function ρ (z).
b) In a static atmosphere, each parcel of air has an internal energy ∆Ei and a gravitational potential energy ∆Eg. To a very good approximation, the air in the atmosphere is an ideal gas with constant specific heat. Using this assumption, the result of part (a), and classical thermodynamics, show that the total energy in a vertical column of atmosphere of cross-sectional area A is given by
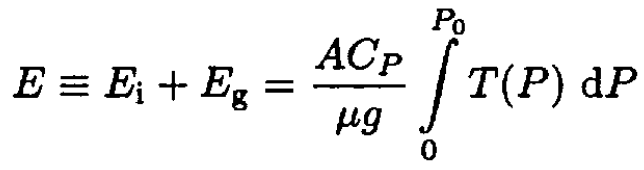
and that the ratio of energies is
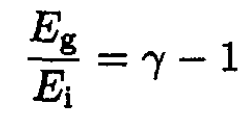
where T is the temperature, P0 is the pressure at the Earth’s surface, μ is the molar mass, Cp is the molar specific heat at constant pressure, and γ ≡ Cp/Cv is the ratio of specific heats.
Hint: The above results do not depend on the specific way in which P(z), T(z) and ρ (z) vary as a function of z (e.g., isothermal, adiabatic, or something intermediate). They depend only on the fact that P(z) is monotonically decreasing. At some step of the derivation, you might find it useful to do an integration by parts.
SOLUTION
a) Again starting with the ideal gas law
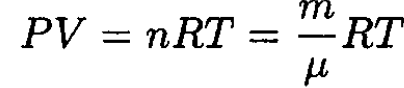
we have
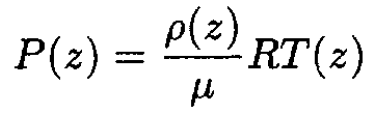 (1)
(1)
b) The gravitational energy of a slice of atmosphere of cross section A and thickness dz at a height z is simply
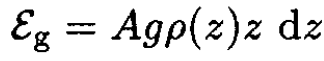 (2)
(2)
while the internal energy of the same slice is
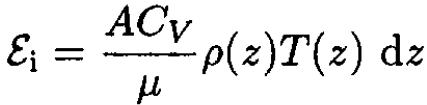 (3)
(3)
The total internal energy Ei is given by the integral of (S.4.21.3):
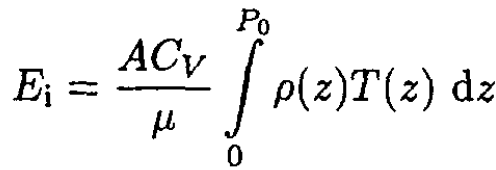 (4)
(4)
We wish to change the integral over z into an integral over P. To do so, first consider the forces on the slice of atmosphere:
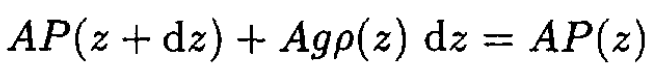 (5)
(5)
Rearranging (5), we have
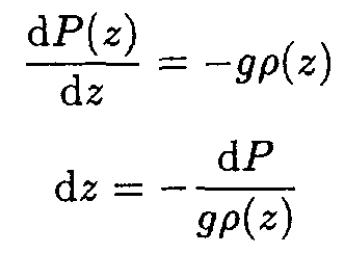 (6)
(6)
Substituting (6) into (4), we obtain
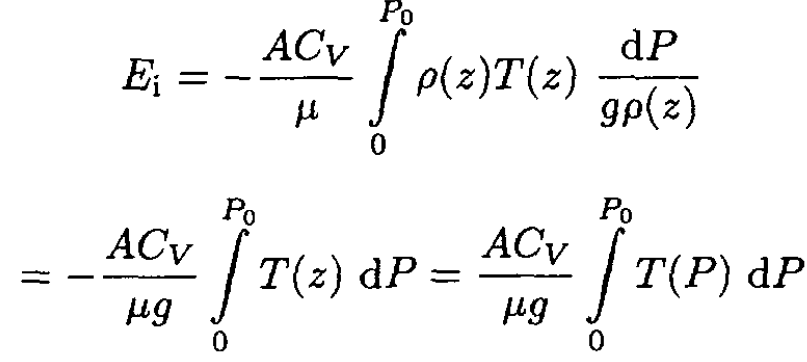 (7)
(7)
The total gravitational energy Eg may be found by integrating (2):
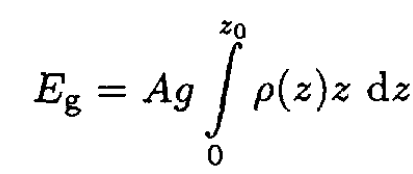 (8)
(8)
Integrating by parts gives
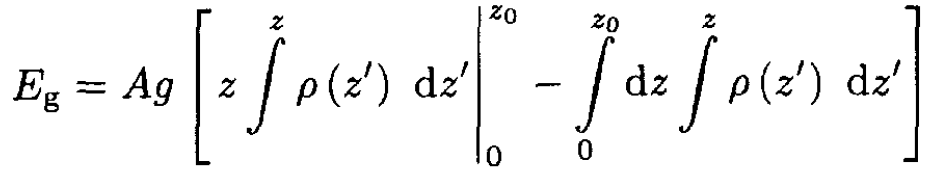 (9)
(9)
The first term on the RHS of (9) is zero since at the limits of evaluation either z = 0 or ∫ ρ (z') = 0, so we have
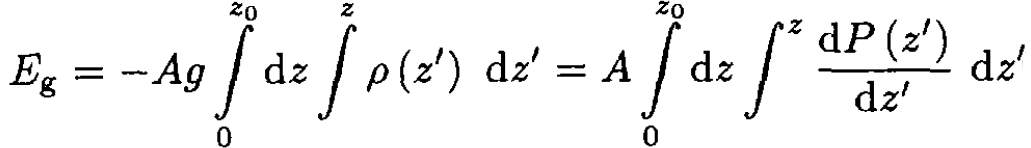 (10)
(10)
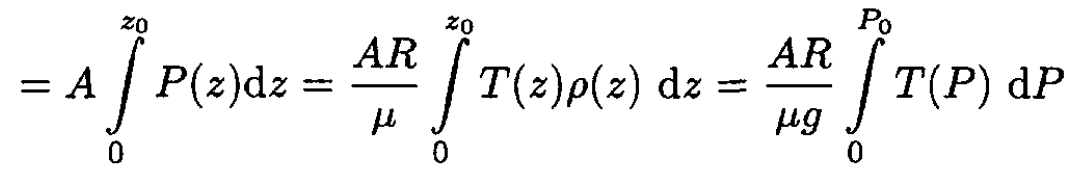
The ratio of energies Eg/Ei, from (10) and (7) is
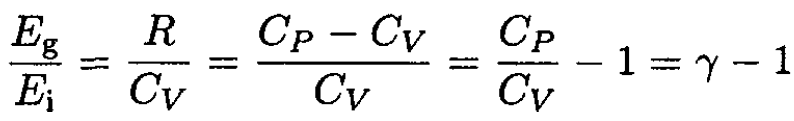 (11)
(11)
Finally,
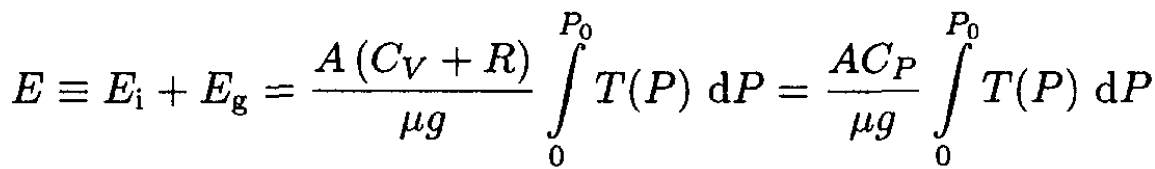 (12)
(12)
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















