
Hydrogen in Capacitor
 المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
 المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
 الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 70
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 70
 18-8-2016
18-8-2016
 1431
1431
Hydrogen in Capacitor
A hydrogen atom in its ground state is placed between the parallel plates of a capacitor. For times t < 0, no voltage is applied. Starting at t = 0,an electric field E(t) = E0e-t/τ is applied, where τ is a constant. Derive the formula for the probability that the electron ends up in state j due to this perturbation. Evaluate the result for j:
a) a 2s state
b) a 2p state
SOLUTION
For time-dependent perturbations a general wave function is
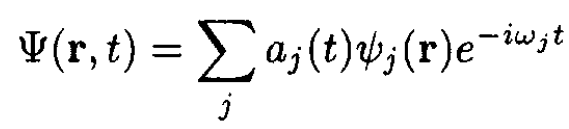 (1)
(1)
where the ѱj satisfy
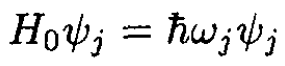 (2)
(2)
For the time-dependent perturbation V(t),
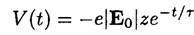 (3)
(3)
From Schrodinger’s equation we can derive an equation for the time development of the amplitudes aj (t):
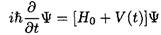 (4)
(4)
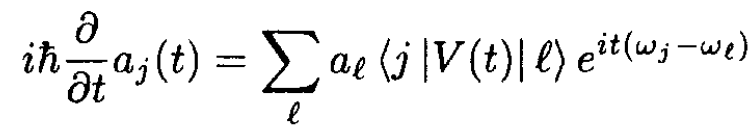 (5)
(5)
If the system is initially in the ground state, we have a1S (0) = 1 and the other values of aj (0) are zero. For small perturbations it is sufficient to solve the equation for j ≠ 1S:
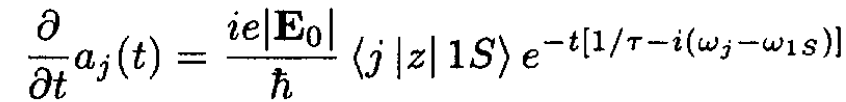 (6)
(6)
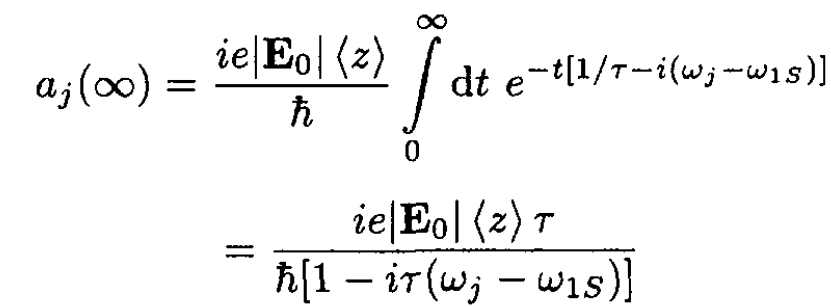 (7)
(7)
The general probability Pj that a transition is made to state j is given by
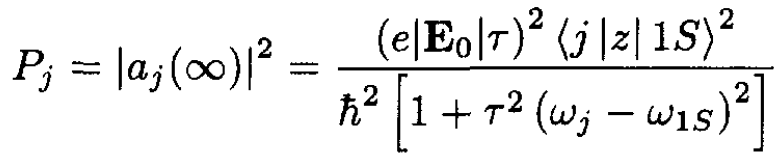 (8)
(8)
This probability is dimensionless. It should be less than unity for this theory to be valid.
a) For the state j = 2S the probability is zero. It vanishes because the matrix element of z is zero: ⟨2S|z|1S⟩ = 0 because of parity. Both S-states have even parity, and z has odd parity.
b) For the state j = 2P the transition is allowed to the L = 1, M = 0 orbital state, which is called 2Pz. The matrix element is similar to the earlier problem for the Stark effect. The 2P eigenstate for L = 1, S = 0 and that for the 1S state is exp 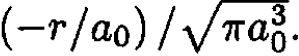 The integral is
The integral is
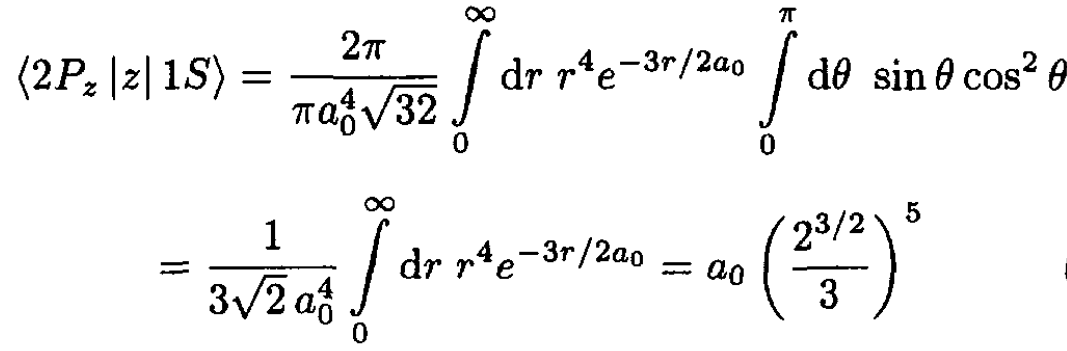 (9)
(9)
where a0 is the Bohr radius of the hydrogen atom.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


