
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Not-so-concentric Spherical Capacitor
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 49
11-8-2016
1936
Not-so-concentric Spherical Capacitor
An insulated metal sphere of radius a with total charge q is placed inside a hollow grounded metal sphere of radius b. The center of the inner sphere is slightly displaced from the center of the outer sphere so that the distance between the two centers is δ (see Figure 1.1).
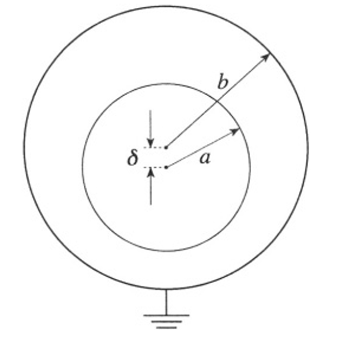
Figure 1.1
a) Use the boundary conditions to determine the potential between the spheres in the case δ = 0.
b) Find the charge distribution of the inner sphere and the force acting on it.
Hint: Show that R(θ) ≈ b + δ cosθ where R is the distance from the center of the inner sphere to the surface of the outer sphere, and write down an expansion for the potential between the spheres using spherical harmonics to first order in δ.
SOLUTION
a) For δ = 0, we have the boundary conditions

 (1)
(1)
which with Gauss’s law yield for the potential between a and b
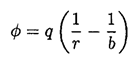
 (2)
(2)
b) Introduce spherical coordinates with the polar axis along the line 
 (see Figure 1.2). Find the equation of the sphere SB in these coordinates.
(see Figure 1.2). Find the equation of the sphere SB in these coordinates.

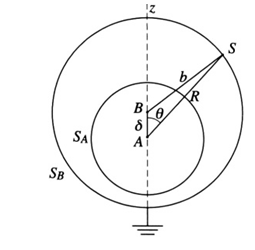
Figure 1.2
From the triangle ∆ABS we have
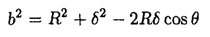

We can expand 1/b as a sum of spherical harmonics using a general formula:
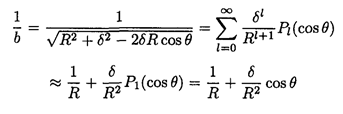

or simply by expanding the square root to first order in δ(δ << R)
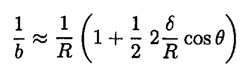

So
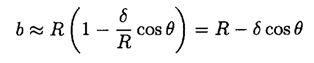
and we have
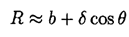
 (3)
(3)
The term δP1 (cosθ) represents the deviation from concentricity and should be zero at δ = 0. We look for a potential as an expansion of spherical harmonics to first order in δ
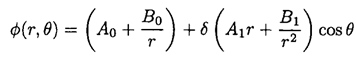
 (4)
(4)
With the boundary conditions in (1)
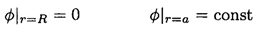

The first term in (4) should be the same as in (a)

We may find A1 and B1 by checking the potential on the inner and outer spheres. On the inner sphere r = a and the potential is a constant, and so must be independent of cosθ. This yields
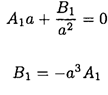
 (5)
(5)
Substituting (5) back into (4), we now check the potential on the outer sphere, where r = b + δ cosθ
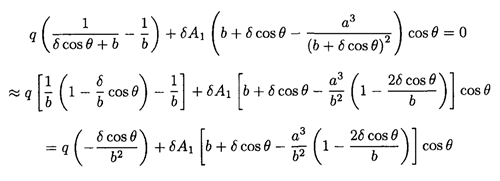

Neglecting terms of order δ2, we find

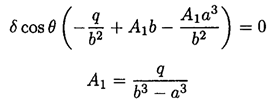
Finally,

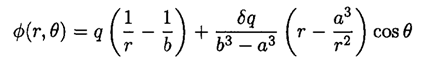
The charge density on the inner sphere is

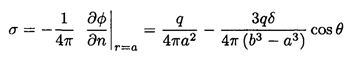
The force on the sphere may now be calculated by integrating the z component of the force on the differential areas of the surface dF = 2πσ2n dA:
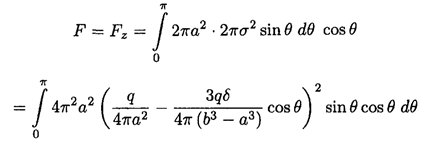

The only term which survives is the cross term
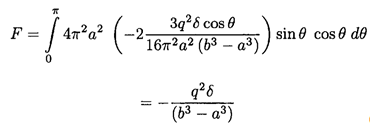
 (6)
(6)
We can check this result in the limit of a = 0 against the force between a charge inside a neutral sphere and the sphere.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















