
Shallow Water Waves
 المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn Boris E. Nadgorny
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn Boris E. Nadgorny
 المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
 الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 28
الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 28
 1-8-2016
1-8-2016
 1461
1461
Shallow Water Waves
Water waves travel on the surface of a large lake of depth d. The lake has a perfectly smooth bottom and the waves are propagating purely in the +z direction (The wave fronts are straight lines parallel to the x axis. See Figure 1.1).
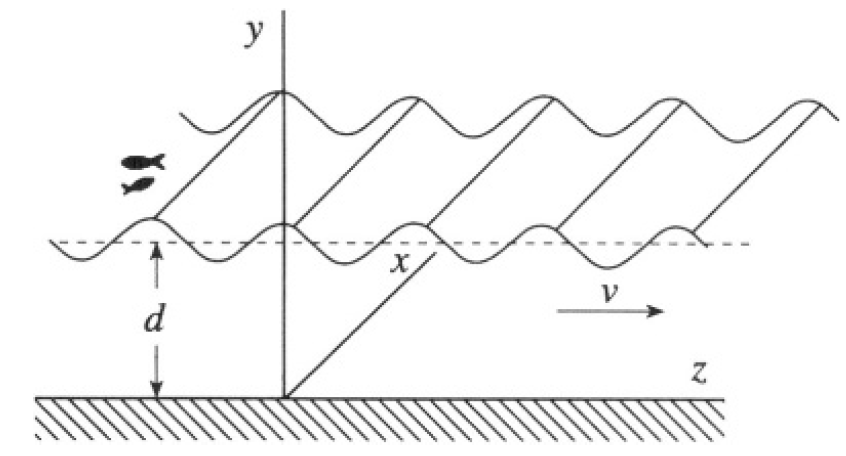
Figure 1.1
a) Find an expression for the velocity of the water v (y, z, t).
b) Find the corresponding dispersion relation. You may assume that the flow of the water is irrotational  that the amplitude of the waves is small (in practice, this means that v2 << gh, where h is the height of the waves), that surface tension effects are not important, and that water is incompressible.
that the amplitude of the waves is small (in practice, this means that v2 << gh, where h is the height of the waves), that surface tension effects are not important, and that water is incompressible.
c) Find the group velocity of the wave front and consider two limiting cases λ >> d, λ << d.
SOLUTION
We essentially follow their solution. In this problem, we consider an incompressible fluid (which implies that the density is constant (see Figure 1.2). We also consider irrotational flow  and ignore the surface tension and viscosity of the fluid. This is a very idealized case. In this case,
and ignore the surface tension and viscosity of the fluid. This is a very idealized case. In this case,
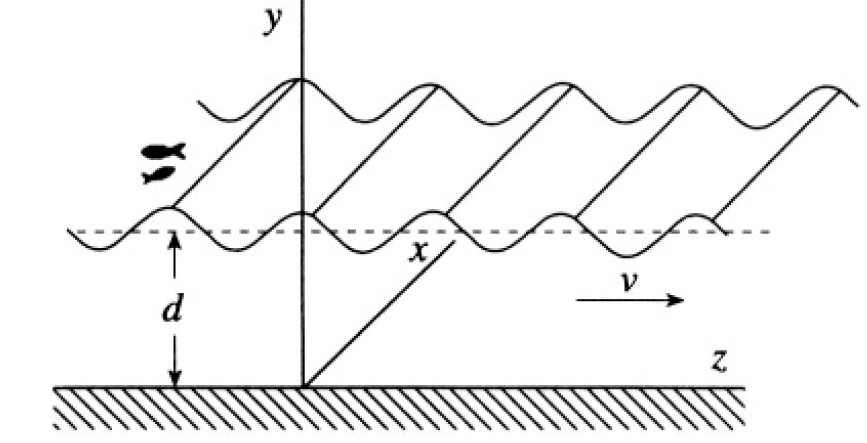
Figure 1.2
we have 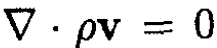 and since ρ is constant,
and since ρ is constant, 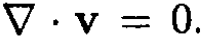 Combining this equation with the condition
Combining this equation with the condition 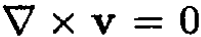 allows us to introduce a potential φ (the so-called potential flow). The velocity v may be written in the form
allows us to introduce a potential φ (the so-called potential flow). The velocity v may be written in the form 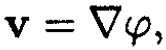 and for the potential we have
and for the potential we have
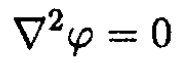 (1)
(1)
On the bottom, we have the boundary condition
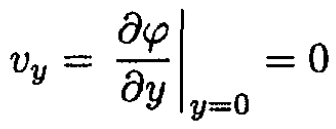 (2)
(2)
Using Euler’s equation for an irrotational field
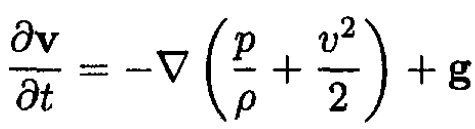 (3)
(3)
(Here p is pressure,  is the acceleration of gravity.) We substitute
is the acceleration of gravity.) We substitute 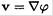 and rewrite (3) as
and rewrite (3) as
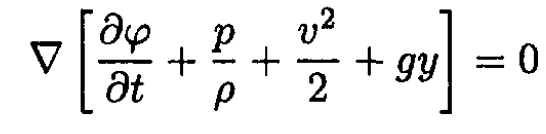 (4)
(4)
Since (4) is the gradient of a function, the function itself will simply be
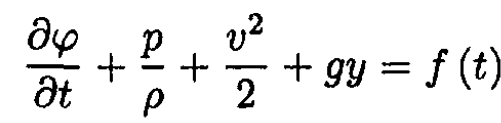
where f(t) is some arbitrary function of time which may be chosen to be zero. Also taking into account that v2/2 << gh, we have
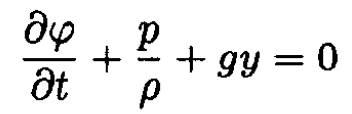
Or
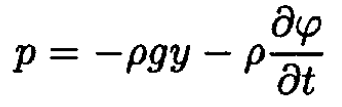 (5)
(5)
Consider the surface of the unperturbed water at y = d and introduce a small vertical displacement Y = y – d. Also, we assume that there is a constant pressure on the surface of the water p. Then from (5) we obtain
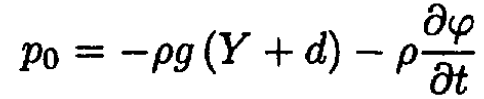 (6)
(6)
The constant p0 + ρgd can be eliminated by using another gauge for φ:
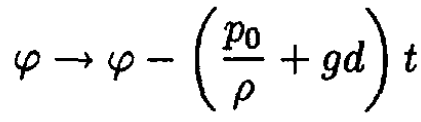
We now obtain from (6)
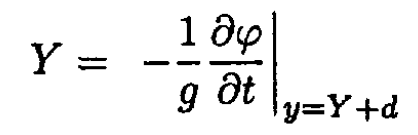 (7)
(7)
Again using the fact that the amplitude of the waves is small, we can write vy = ∂Y/∂t. In the same approximation of small oscillations, we can take the derivative at y = d. On the other hand, vy = ∂φ/∂y. So, from (7)
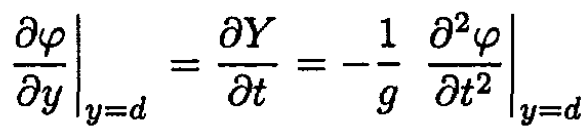 (8)
(8)
Now look for a solution for φ in the form φ = f(y) cos (kz – ωt). Substituting this into (1) gives
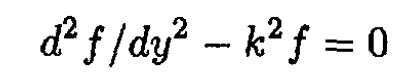 (9)
(9)
so
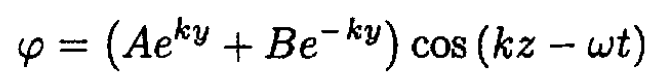 (10)
(10)
where A, B are arbitrary constants. From (2), we find that A = B and φ = A' cos h ky . cos(kz – ωt) where A' = 2A. By differentiating the potential we obtain the velocity components
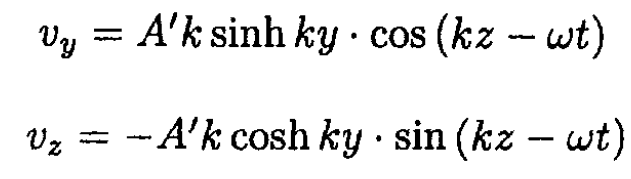
b) From (8) we get the dispersion relation:
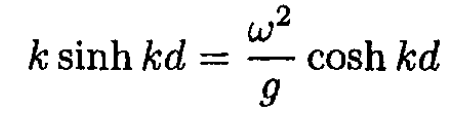 (11)
(11)
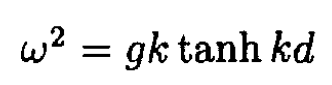 (12)
(12)
c) The group velocity of the waves is
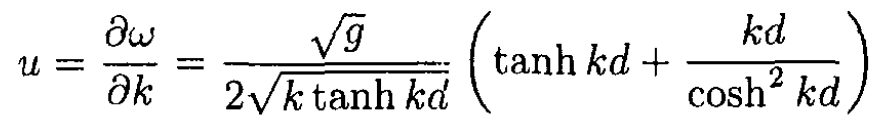 (13)
(13)
Consider two limiting cases:
1) kd >> 1, d >> λ short wavelength waves. Then
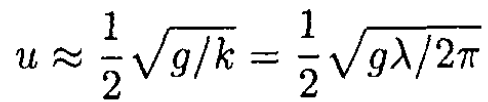
2) kd << 1, d << λ long wavelength waves. Then 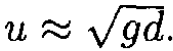
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


