
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Positronium and Relativistic Doppler Effect
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 39
13-7-2016
1705
Positronium and Relativistic Doppler Effect
An electron e- and a positron, e+, each of mass me, bound with binding energy εb in positronium, annihilate into two photons.
a) Calculate the energy, momentum, velocity, and frequency of the photons.
b) The positronium with velocity v moves away from the observer in the lab and annihilates as shown in Figure 1.1. Give the frequency of the photon as measured by the observer and calculate its frequency in terms of the frequency in the positronium rest system (Relativistic Doppler Effect).
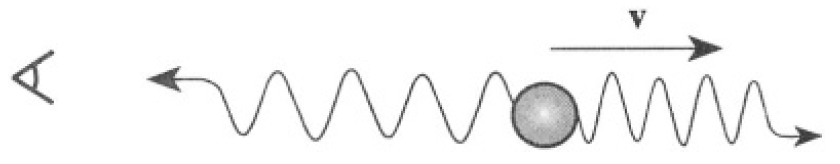
Figure 1.1
SOLUTION
a) The two photons will have momenta p of the same magnitude (but opposite sign), so their energies ε are also the same:
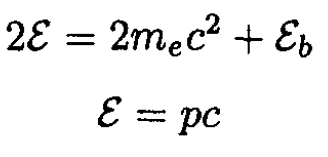
where we have chosen their momenta to be along the x axis. From these formulas we can find
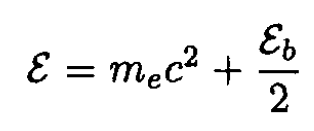 (1)
(1)
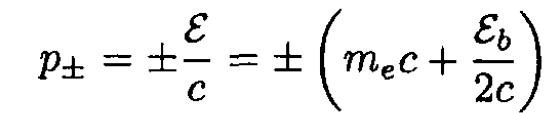 (2)
(2)
The frequency of the photons is
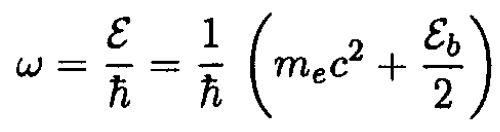 (3)
(3)
The velocity of the photon is, of course, u = ± c.
b) To find the velocity and the frequency of the photon in the lab frame we can use the Lorentz transformations for momentum and energy for the photon that is registered by the observer (with momentum p- from (2)):
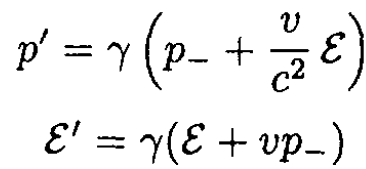
where ε, p are the energy and momentum of the photon in the rest frame, and ε', p' are the energy and momentum of the photon in the observer’s frame.
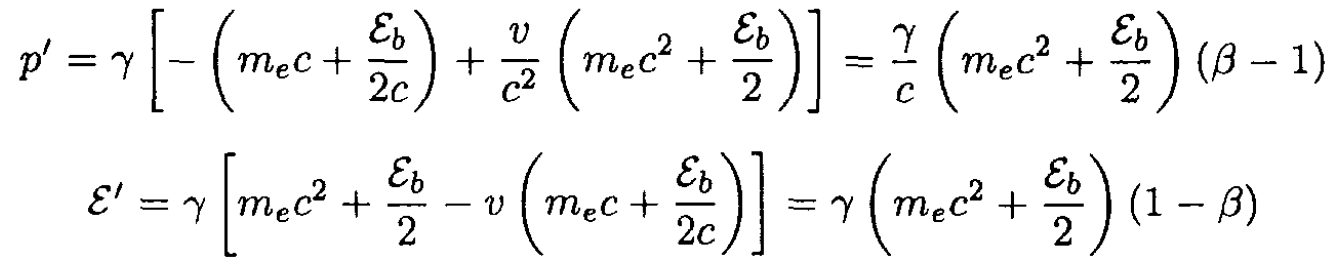
so the velocity of the photon in the observer’s frame is u' = p'c2/ε' = - c, which of course is what one would expect. The frequency of the photon measured by the observer is
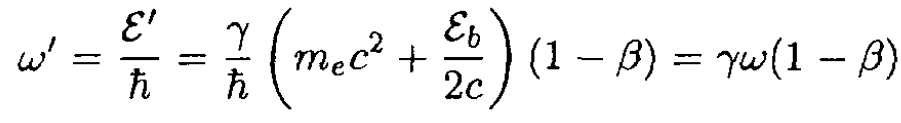
where we substitute ω from (3) of (a). So the original frequency is redshifted to
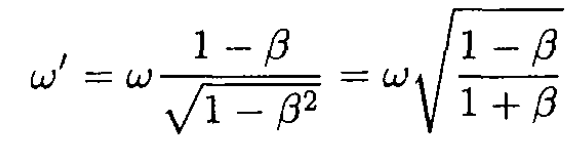
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















