


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
أقرأ أيضاً
التاريخ: 10-7-2016
التاريخ: 2025-03-20
التاريخ: 22-5-2016
التاريخ: 1-2-2022
|
Here we note the interesting fact that the numerator in the exponent of Eq. (40.1) is the potential energy of an atom.

Therefore, we can also state this particular law as: the density at any point is proportional to
e−the potential energy of each atom/kT.
That may be an accident, i.e., may be true only for this particular case of a uniform gravitational field. However, we can show that it is a more general proposition. Suppose that there were some kinds of force other than gravity acting on the molecules in a gas. For example, the molecules may be charged electrically, and may be acted on by an electric field or another charge that attracts them. Or, because of the mutual attractions of the atoms for each other, or for the wall, or for a solid, or something, there is some force of attraction which varies with position and which acts on all the molecules. Now suppose, for simplicity, that the molecules are all the same, and that the force acts on each individual one, so that the total force on a piece of gas would be simply the number of molecules times the force on each one. To avoid unnecessary complication, let us choose a coordinate system with the x-axis in the direction of the force, F.
In the same manner as before, if we take two parallel planes in the gas, separated by a distance dx, then the force on each atom, times the n atoms per cm³ (the generalization of the previous nmg), times dx, must be balanced by the pressure change: Fndx=dP=kTdn. Or, to put this law in a form which will be useful to us later,
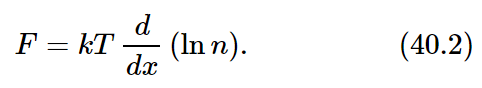
For the present, observe that −Fdx is the work we would do in taking a molecule from x to x+dx, and if F comes from a potential, i.e., if the work done can be represented by a potential energy at all, then this would also be the difference in the potential energy (P.E.). The negative differential of potential energy is the work done, Fdx, and we find that d(lnn)=−d(P.E.)/kT, or, after integrating,
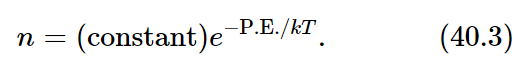
Therefore, what we noticed in a special case turns out to be true in general. (What if F does not come from a potential? Then (40.2) has no solution at all. Energy can be generated, or lost by the atoms running around in cyclic paths for which the work done is not zero, and no equilibrium can be maintained at all. Thermal equilibrium cannot exist if the external forces on the atoms are not conservative.) Equation (40.3), known as Boltzmann’s law, is another of the principles of statistical mechanics: that the probability of finding molecules in a given spatial arrangement varies exponentially with the negative of the potential energy of that arrangement, divided by kT.
This, then, could tell us the distribution of molecules: Suppose that we had a positive ion in a liquid, attracting negative ions around it, how many of them would be at different distances? If the potential energy is known as a function of distance, then the proportion of them at different distances is given by this law, and so on, through many applications.



|
|
|
|
لخفض ضغط الدم.. دراسة تحدد "تمارين مهمة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مشاتل الكفيل تزيّن مجمّع أبي الفضل العبّاس (عليه السلام) بالورد استعدادًا لحفل التخرج المركزي
|
|
|