


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 23-10-2015
Date: 22-10-2015
Date: 23-10-2015
|
Born: 1499 in Jauer, Silesia (now Jawor, Poland)
Died: 1543 in Vienna, Austria
 Little is known about Christoff Rudolff's origins, family and school education. However, Wolfgang Kaunzner's research has come up with a possible lead [11]:-
Little is known about Christoff Rudolff's origins, family and school education. However, Wolfgang Kaunzner's research has come up with a possible lead [11]:-
In the summer semester of 1493 Cristoferus Valentini de Jauer matriculated at the University Krakow and he received a baccalaureate degree in 1495 as Cristophorus de Jauer. It is possibly that this is a relative of Rudolff's or even Rudolff himself.
The town of Jauer, in which he was born, was culturally Polish but had been under the control of the Bohemians since 1335. It would appear that Rudolff's mother tongue was German and, during his lifetime, Jauer came under Austrian Habsburgs control in 1526. By this time, however, he was living in Vienna. In fact he studied algebra in Vienna between 1517 and 1521. His teacher there was Heinrich Schreyber from Erfurt, who is better known by his Latin name Henricus Grammateus. Schreyber taught at the University of Vienna between 1517 and 1521, so we know that Rudolff must have studied there for some period before 1521. He remained in Vienna after studying at the university and earned his living giving private lessons in mathematics. He did use the facilities offered by the university, being able to use books in the university library and talking with academics at the university. However, he never held an official position at the university and characterised himself, in the Foreword of one of his books, as:-
... an amateur of the liberal arts.
Rudolff's book Coss, written in 1525, is the first German algebra book. The book was dedicated to the bishop of Brixen (still known as Brixen to the German speaking population, but now the town is in Italy and known as Bressanone in Italian). At this time Brixen was controlled by the Habsburgs and this dedication makes one wonder whether Rudolff had spent some time there. The reason for the title is that 'cosa' is a 'thing' which was used for the unknown. For many years algebraists were called cossists and algebra was known as the cossic art. Although this is the first German algebra book, containing some important innovations, there were already a number of algebra books (some only existing in manuscript) which Rudolff had studied before writing his text. These included Robert of Chester's translation of al-Khwarizmi's Hisab al-jabr w'al-muqabala, which was available in manuscript form, and he used a compilation of algebra texts by Johann Vögelin who worked in Vienna. Rudolff uses letters for algebraic quantities, unlike early algebra texts as he points out in Coss:-
This is evident from old books on algebra, written many years ago, in which quantities are represented, not by characters, but by words written out in full, 'drachm', 'thing', 'substance', etc., and in the solution of each special example the statement was put, 'one thing', in such words as ponatur, una res, etc.
From this quote we see that he must have read the Latin Regensburg algebra of 1461 for in that work the solution to all problems begin with the words 'Pono quod lucrum sit una res'. We will return to look at the contents of Coss in a moment, but first let us look at Rudolff's other works.
In 1526, the year after Coss appeared, Rudolff produced Künstliche Rechnung mit der Ziffer und mit den Zahlpfennigen. This work studied applications of mathematics to commerce and industry. Of course, the beginning of the 16th century saw the cottage industries of earlier times replaced by larger scale manufacturing ventures which required considerably more management and financial control thus leading to a much greater need for arithmetical skills. The book was divided into three parts. The first part, Grundbüchlein, introduced the reader to methods of calculating with whole numbers and with fractions. Both methods of calculating using an abacus and methods of calculating without using the abacus are given. The second part, Regelbüchlein, teaches the reader the 'Regel de Tri', the 'rule of three' or the rule of proportionality, and the 'Wellischen Practica', the 'Welsch practice' which was an Italian method for solving applied arithmetical problems. The third part of the book, Exempelbüchlein, contains around 300 problems and results which concentrate on the needs of those working in commercial or manufacturing organisations. The book, however, also contains some applications to mathematical recreations.
In 1530 Rudolff produced the book Exempelbüchlin which has much in common with the third part of his earlier work and contains 293 problems. This book, published in Augsburg, is important for it is the first work in which one finds calculations with decimal fractions. His notation for decimals is not very different from that used today; instead of the modern "decimal point", Rudolff uses a bar to separate the integral and fractional parts. David Smith writes [13]:-
In this work [Rudolff] solved an example in compound interest, and used the bar precisely as we should use a decimal point today. If any particular individual were to be named as having the best reason to be called the inventor of decimal fractions, Rudolff would seem to be the man, because he apparently knew how to operate with these forms as well as merely to write them, as various predecessors had done. His work, however, was not appreciated, and apparently was not understood, and it was not until 1585 that a book upon the subject appeared.
Kurt Vogel explains in [1] that, as well as the collection of arithmetical problems, the book contains:-
... tables of measurements for many regions, a list of symbols used in gauging, and numerous hints for solving problems.
Let us return to Rudolff's Coss and, first, give its full title: Behend vnnd Hubsch Rechnung durch die kunstreichen regeln Algebre so gemeinlicklich die Coss genent werden. The book was published in Strassburg. We noted above some of the manuscripts on algebra which Rudolff had read before producing his book and in fact many of his fellow mathematicians criticised him for 'stealing' his examples from earlier texts. It was standard practice at this time, and for many years after this, to use examples from earlier works and Michael Stifel strongly defends Rudolff from these attacks. It is reasonable to believe that Rudolff's fellow mathematicians were upset at this book because it was written in German rather than Latin.
There are two parts to the book: the first part contains twelve chapters and this material, writes Rudolff, must be mastered by the reader before he progresses to a study of algebra which comprises the second part of the book. What, then, must the reader master before beginning algebra? The chapters contain explanations of how to calculate with numbers, both whole numbers and fractions, then the famous rule of three is explained followed by methods to compute square roots and cube roots of numbers. He used √ for square roots (the first to use this notation), 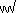 for cube roots and
for cube roots and 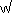 for 4th roots. This does seem a little strange and Stifel thought so since he adopted
for 4th roots. This does seem a little strange and Stifel thought so since he adopted 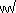 for cube roots and
for cube roots and 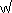 for 4th roots in his second edition of Coss. Returning to the first edition, Rudolff computes with expressions involving square roots. For example he subtracts 5 + √8 from 12 + √128 to get 7 + √72. Slightly more difficult is his example (√50 - 2) - (√32 - 5 ) = √2 + 3 and then, after examples of increasing difficulty, ends with (√450 - √18) - (√32 + √8) = √72. Next come formulas for summing arithmetic and geometric series. This takes us to the end of the fourth chapter of part 1. Beginning with chapter 5 he considers algebraic expressions. Where we would write: 1, x, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9 Rudolff writes a list of ten, essentially different, symbols. Opposite each symbol is its name (we give our modern symbol and Rudolff's name for the first few entries):
for 4th roots in his second edition of Coss. Returning to the first edition, Rudolff computes with expressions involving square roots. For example he subtracts 5 + √8 from 12 + √128 to get 7 + √72. Slightly more difficult is his example (√50 - 2) - (√32 - 5 ) = √2 + 3 and then, after examples of increasing difficulty, ends with (√450 - √18) - (√32 + √8) = √72. Next come formulas for summing arithmetic and geometric series. This takes us to the end of the fourth chapter of part 1. Beginning with chapter 5 he considers algebraic expressions. Where we would write: 1, x, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9 Rudolff writes a list of ten, essentially different, symbols. Opposite each symbol is its name (we give our modern symbol and Rudolff's name for the first few entries):
1 - Dragma or numerus
x - radix
x2 - zensus
x3 - cubus
x4 - zensdezens
The list goes up to x9 which is named cubus de cubo. Under the list Rudolff writes:-
Dragma or numerus is taken here as 1. It is no number, but assigns other numbers their kind. Radix is the side or root of a square. Zensus, the third in order, is always a square; it arises from the multiplication of the radix into itself. Thus, when radix means 2, then 4 is the zensus.
Rudolff goes on to look at adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing polynomial expressions. Using modern notation for powers of the unknown, rather than those of Rudolff, we see that he gets quite far as the following example shows:
12/(x + 2) - (x - 2)/12 = (148 - x2)/(12x + 24).
The second part of Rudolff's Coss contains three chapters. The first of these gives methods for solving linear and quadratic equations. Earlier works on solving equations had presented the reader with 24 different cases but Rudolff reduces this to 8 cases. In looking at the case of a quadratic of the form ax2 + b = cxhe believed at first that there was only one solution to this equation which will solve the original problem, but he later recognised his error and realised that such equations have two solutions. The second chapter is again concerned with solving equations and presents rules for solving them. The third chapter, like the final chapter to the first part, presents examples; in this part of the work there are over 400 of them [1]:-
Some of the problems involve abstract numbers; others, taken from daily life, are presented in fantastic forms similar to those of the 'Enigmata' of recreational mathematics. In some of the problems Rudolff introduces a second unknown, q (for 'quantitas'). If there are more unknowns than equations, the problem is considered indeterminate. For several such problems concerned with "splitting the bill" (Zechenaufgaben) Rudolff supplied all the possible solutions. The 'Coss' ends with three cubic problems. Rudolff does not work out their solutions because, as he stated, he wanted to stimulate further algebraic research.
There are some other features of Coss that are worth mentioning. He introduced the notation
√.12 + √140
to mean √(12 + √140) and so distinguish it from √12 + √140. Later authors added a second dot to indicate how far the square root extended (giving the dots precisely the meaning of the brackets we have used. Another important feature of Coss is that Rudolff uses letters to represent numbers. Earlier cossists had only used letters for the unknown. To indicate exactly how Rudolff did this we give an example from the book:-
Take 1/2 this sum, assume for it a position, which, being empty, is called c. Then subtract c from a, what remains call d. Now I say that √c + √d is the square root of the first binomial.
Kurt Vogel evaluates Rudolff's importance in [1]:-
Rudolff's importance in the history of mathematics lies in his having written the first comprehensive book on algebra in German. In this work he went far beyond his teacher Grammateus, especially concerning calculation with rational and irrational polynomials. Rudolff was aware of the double root of the equation ax2 + b = cx and gave all the solutions to indeterminate first-degree equations. His writings are remarkable both for the occasional appearance of decimal fractions and for improvements in symbolism. Adding a diagonal stroke to the points used by earlier cossists, Rudolff introduced ... signs ... for the second, third, and fourth roots. His work also gives a hint of the beginnings of exponential arithmetic and the fundamental idea of logarithms - that is, setting x0 equal to 1. His methodical hints on using the Coss are worth noting as well. In brief, Rudolff's role in the development of mathematical studies in Germany was analogous to that of Fibonacci in Italy.
As to his influence on later mathematicians, we note that Michael Stifel brought out a new addition to Rudolff's Coss in 1553, adding some important material of his own. In [10] Albrecht Heeffer identifies Rudolff's Coss as the source of most of the problems in the first volume of Euler's Vollständige Anleitung zur Algebra (1770). In fact when Euler was learning mathematics he made a careful study of Rudolff's work.
Books:
Articles:



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|