


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 19-11-2021
Date: 10-12-2021
Date: 13-9-2021
|
Vitamin K : Function
The principal role of vitamin K is in the posttranslational modification of a number of proteins (most of which are involved with blood clotting), in which it serves as a coenzyme in the carboxylation of certain glutamic acid residues in these proteins. Vitamin K exists in several active forms, for example, in plants as phylloquinone (or vitamin K1), and in intestinal bacteria as menaquinone (or vitamin K2). A synthetic form of vitamin K, menadione, is able to be converted to K2.
Function
1. γ-Carboxyglutamate formation: Vitamin K is required in the hepatic synthesis of the blood clotting proteins, prothrombin (factor [F]II) and FVII, FIX, and FX. Formation of the functional clotting factors requires the vitamin K–dependent carboxylation of several glutamic acid residues to γ-carboxyglutamate (Gla) residues (Fig.1). The carboxylation reaction requires γ-glutamyl carboxylase, O2, CO2, and the hydroquinone form of vitamin K (which gets oxidized to the epoxide form). The formation of Gla residues is sensitive to inhibition by warfarin, a synthetic analog of vitamin K that inhibits vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR), the enzyme required to regenerate the functional hydroquinone form of vitamin K.
Figure 1: Carboxylation of glutamate to form γ-carboxyglutamate. h = hydroquinone; e = epoxide; VKOR = vitamin K epoxide reductase.
2. Prothrombin interaction with membranes: The Gla residues are good chelators of positively charged calcium ions, because of their two adjacent, negatively charged carboxylate groups. With prothrombin, for example, the prothrombin–calcium complex is able to bind to negatively charged membrane phospholipids on the surface of damaged endothelium and platelets. Attachment to membrane increases the rate at which the proteolytic conversion of prothrombin to thrombin can occur (Fig. 2).
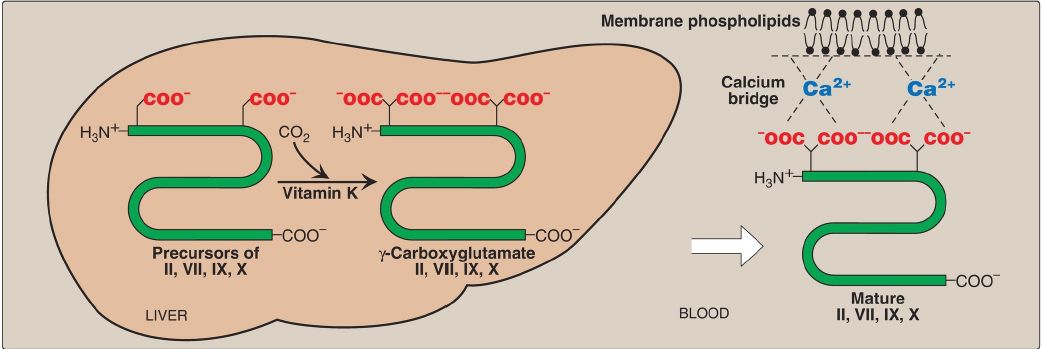
Figure 2: Role of vitamin K in blood coagulation. CO2 = carbon dioxide.
3. γ-Carboxyglutamate residues in other proteins: Gla residues are also present in proteins other than those involved in forming a blood clot. For example, osteocalcin and matrix Gla protein of bone and proteins C and S (involved in limiting the formation of blood clots) also undergo γ-carboxylation.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
سماحة السيد الصافي يؤكد ضرورة تعريف المجتمعات بأهمية مبادئ أهل البيت (عليهم السلام) في إيجاد حلول للمشاكل الاجتماعية
|
|
|