


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 15-9-2021
Date: 26-9-2021
Date: 14-9-2021
|
Homocystinuria
The homocystinurias are a group of disorders involving defects in the metabolism of Hcy. These autosomal-recessive diseases are characterized by high urinary levels of Hcy, high plasma levels of Hcy and methionine, and low plasma levels of cysteine. The most common cause of homocystinuria is a defect in the enzyme cystathionine β-synthase, which converts Hcy to cystathionine (Fig. 1). Individuals homozygous for cystathionine β-synthase deficiency exhibit dislocation of the lens (ectopia lentis), skeletal anomalies (long limbs and fingers), intellectual disability, and an increased risk for developing thrombi (blood clots).
Thrombosis is the major cause of early death in these individuals. Treatment includes restriction of methionine and supplementation with vitamin B12 and folate. Additionally, some patients are responsive to oral administration of pyridoxine (vitamin B6), which is converted to pyridoxal phosphate, the coenzyme of cystathionine β-synthase. These patients usually have a milder and later onset of clinical symptoms compared with B6-nonresponsive patients. [Note: Deficiencies in methylcobalamin or N5,N10-MTHF reductase ([MTHFR]; ) also result in elevated Hcy.]
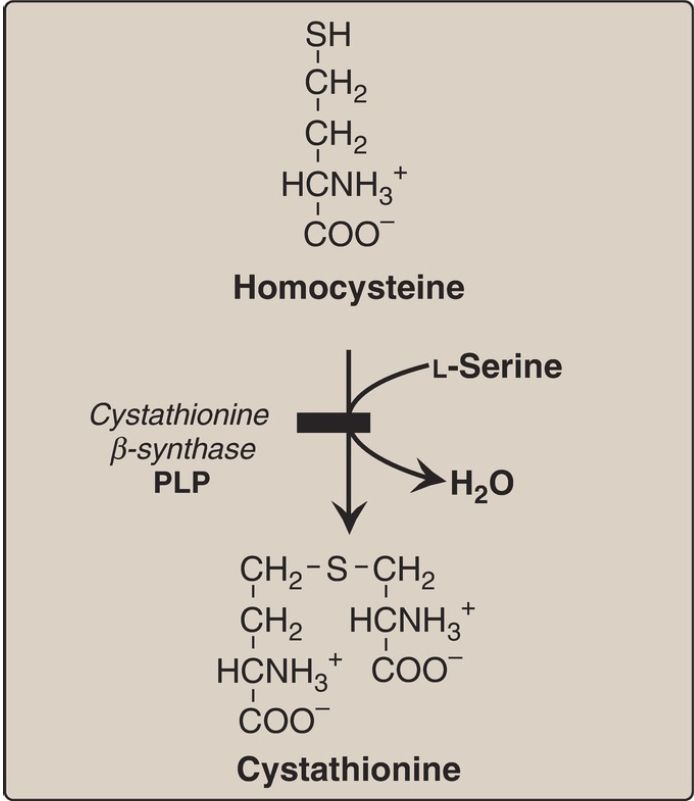
Figure 1: Enzyme deficiency in homocystinuria. PLP = pyridoxal phosphate.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|