


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 9-9-2021
Date: 29-12-2021
Date: 25-12-2021
|
Proteoglycans
Proteoglycans are found in the ECM and on the outer surface of cells.
1. Monomer structure: A proteoglycan monomer found in cartilage consists of a core protein to which up to 100 linear chains of GAG are covalently attached. These chains, which may each be composed of up to 200 disaccharide units, extend out from the core protein and remain separated from each other because of charge repulsion. The resulting structure resembles a bottle brush (Fig. 1).
In cartilage proteoglycans, the species of GAG include chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate. [Note: Proteoglycans are grouped into gene families that encode core proteins with common structural features. The aggrecan family (aggrecan, versican, neurocan, and brevican), abundant in cartilage, is an example.]
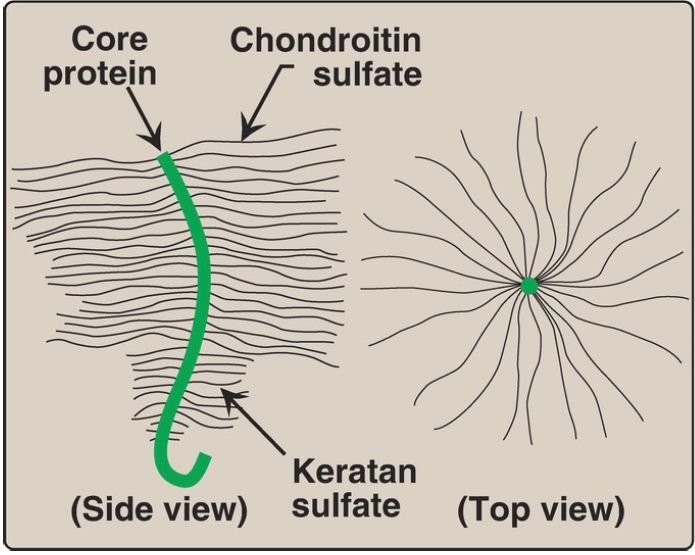
Figure 1 : Bottle brush model of a cartilage proteoglycan monomer.
2. GAG–protein linkage: This covalent linkage is most commonly through a trihexoside (galactose-galactose-xylose) and a serine residue in the protein. An O-glycosidic bond is formed between the xylose and the hydroxyl group of the serine (Fig. 2).
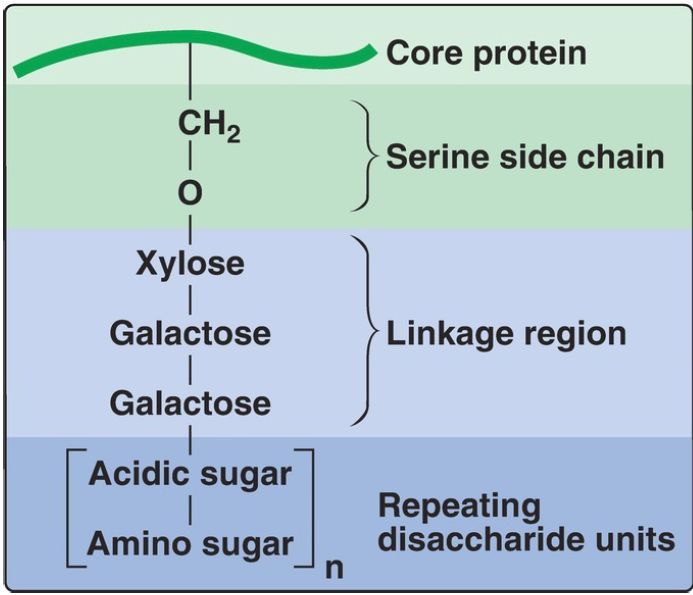
Figure 2: Glycosaminoglycan linkage regions.
3. Aggregate formation: Many proteoglycan monomers can associate with one molecule of hyaluronic acid to form proteoglycan aggregates. The association is not covalent and occurs primarily through ionic interactions between the core protein and the hyaluronic acid. The association is stabilized by additional small proteins called link proteins (Fig. 3).
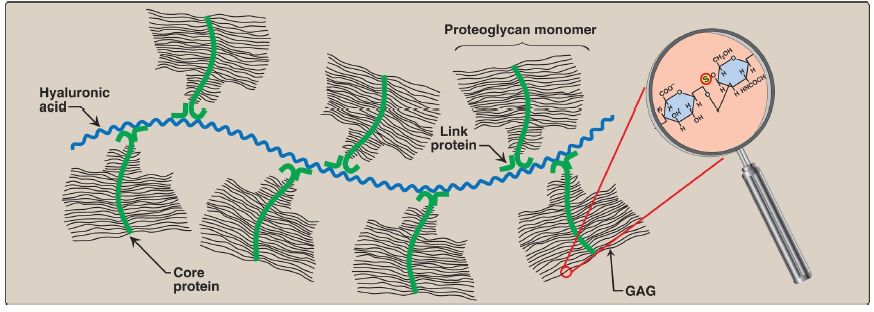 Figure 3: Proteoglycan aggregate. GAG = glycosaminoglycan.
Figure 3: Proteoglycan aggregate. GAG = glycosaminoglycan.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|