


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 21-12-2020
Date: 18-2-2021
Date: 13-2-2021
|
Stray-field methods
The first method for visualizing domains was developed in the 1930s by Francis Bitter. A magnetic colloid, normally a drop of oil- or water-based ferrofluid
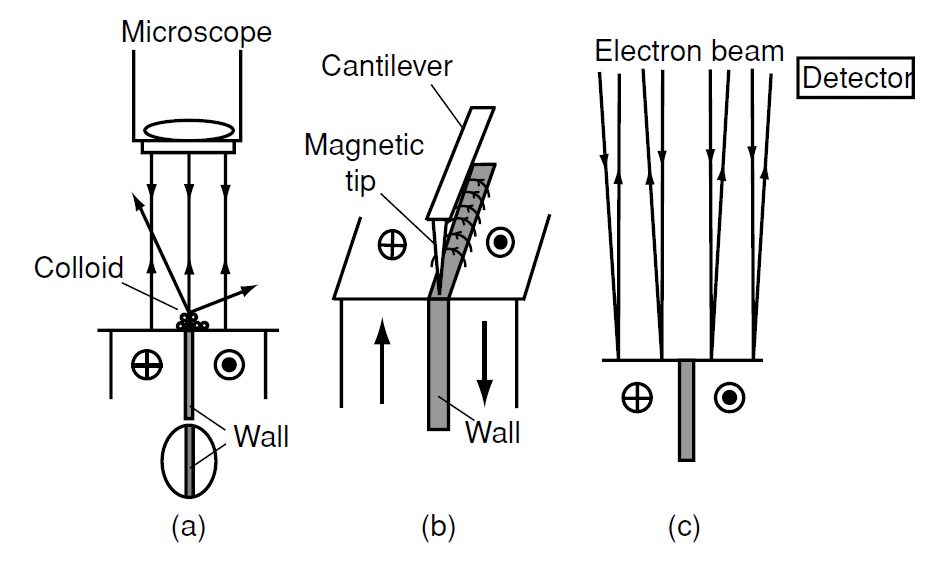
Figure 1: Stray-field methods of domain observation: (a) Bitter method, (b) MFM and (c) SEM with type 1 contrast.
is spread over the polished surface of a specimen, and the tiny ferromagnetic particles are drawn to the regions of maximum field gradient, thereby decorating the domain walls (Fig. 1).
The modern method of measuring stray fields is a scanning probe technique based in the same principle – magnetic force microscopy (MFM). A single ferromagnetic particle is mounted on a tiny silicon cantilever, or the tip of the cantilever is coated with a ferromagnetic film and it is rastered across the surface of the sample. The force derivative registered by the deflection of the cantilever or the change of its mechanical resonance frequency gives an image of the stray field gradient at the surface. The resolution achievable with MFM is about 20 nm. A problem arises when imaging soft magnetic materials, because the stray field produced by the tip may perturb the domain structure of the sample.
Reading magnetically recorded information from discs or tapes likewise depends on sensing the stray field distribution of the domain pattern imposed on the magnetic medium, using an inductive or magnetoresistive pick-up head.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is a workhorse of materials science. It involves rastering a sample surface with a finely focussed electron beam and detecting the secondary electrons emitted from the surface. SEM is used to image both microstructure and topology, and can provide chemical analysis on a local scale because the energies of the secondary electrons and especially those of the accompanying X-rays are characteristic of the chemical elements present. Sensitivity is good for elements with 3s and deeper electronic shells (Na and beyond). Lower-energy X-rays from light elements can be observed with a special windowless detector. SEM can be adapted to provide magnetic contrast by detecting the deflection of the secondary electrons in the stray field produced near the surface of a multidomain sample. Alternatively, the spin polarization of the secondary electrons can be monitored as the electron beam is rastered across the surface, a technique known as scanning electron microscopy with polarization analysis (SEMPA).



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|