


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 7-3-2016
Date: 15-11-2020
Date: 7-3-2016
|
REFLECTION OF LIGHT
We can begin to understand the reflection of visible light from a smooth metal surface. Suppose we have a long wavelength wave impinging on a metal surface represented by a regular array of atoms, as illustrated in Figure (1). As the wave passes over the array of atoms, circular scattered waves emerge. As seen in Figure (1a), the scattered waves add up to produce a reflected wave coming back out of the surface. The angles labeled θi and θr in Figure (1b) are what are called the angle of incidence and angle of reflection , respectively. Since the scattered waves emerge at the same speed as the incident wave enters, it is clear from the geometry that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. That is the main rule governing the reflection of light.
What happens inside the material depends upon details of the scattering process. Note that the reflected wavefront inside the material coincides with the incident wave. For a metal surface, the phases of the scattered waves are such that the reflected wave inside just cancels the incident wave and there is no wave inside. All the radiation is reflected. For other types of material that are not opaque, the incident and scattered

Figure 1a: A reflected wave is produced when the incident wave is scattered by many atoms. From this diagram, you can see why the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
waves do not cancel. Instead they add up to produce a new, transmitted wave whose crests move slower than the speed of light. This apparent slowing of the speed of light, due to the interference of transmitted and scattered waves, leads to the bending of a beam of light as it enters or leaves a transparent medium. It is this bending that allows one to construct lenses and optical instruments.
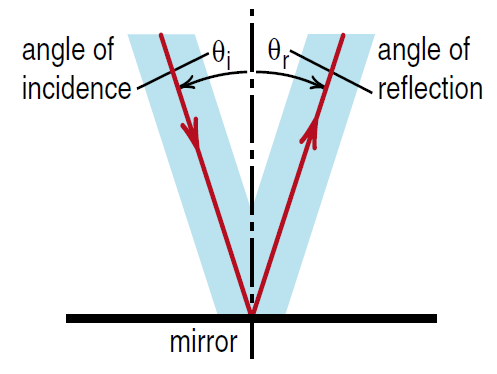
Figure 1b: When light reflects from a mirror, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|