


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 30-11-2020
Date: 29-12-2016
Date: 11-3-2021
|
Bicycle Wheel
For much of the remainder of the chapter, we will use a bicycle wheel, often weighted with wire wound around the rim, to illustrate various phenomena of rotational motion. Conceptually we can think of the bicycle wheel as a collection of masses on the ends of massless rods as shown in Figure (2). The massless rods form the spokes of the wheel, and we can think of the masses m as fusing together to form the wheel.
When forming a wheel, all the masses have the same radius r, same angular velocity ω and same angular acceleration α . If we choose one point on the wheel from which to measure the angular distance θ, then as far as angular motion is concerned, it does not make any difference whether we are discussing the mass on the end of a rod shown in Figure (1) or the bicycle wheel shown in Figure (2). Which model we use depends upon which provides a clearer insight into the phenomena being discussed.
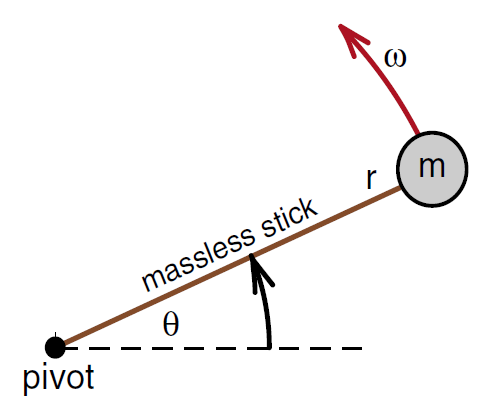
Figure 1: Mass rotating on the end of a massless stick.
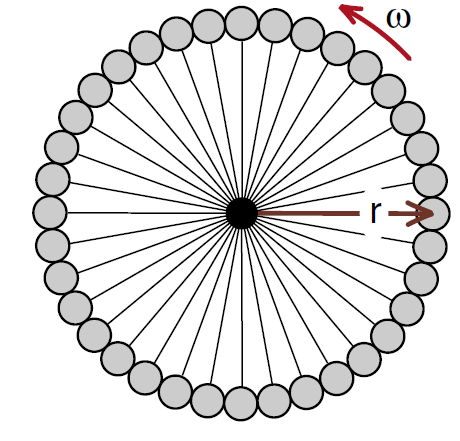
Figure 2: Bicycle wheel as a collection of masses on the end of massless rods.



|
|
|
|
"إنقاص الوزن".. مشروب تقليدي قد يتفوق على حقن "أوزيمبيك"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الصين تحقق اختراقا بطائرة مسيرة مزودة بالذكاء الاصطناعي
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ووفد من جامعة البصرة يبحثان سبل تعزيز التعاون المشترك
|
|
|