
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
THE FAHRENHEIT SCALE
المؤلف:
S. Gibilisco
المصدر:
Physics Demystified
الجزء والصفحة:
p 273
2087
THE FAHRENHEIT SCALE
In much of the English-speaking world, and especially in the United States, the Fahrenheit temperature scale (°F) is used by laypeople. A Fahrenheit degree is the same size as a Rankine degree. However, the scale is situated differently. The melting temperature of pure water ice at sea level is +32°F, and the boiling point of pure liquid water is +212°F. Thus, + 32°F corresponds to 0°C, and +212°F corresponds to +100°C. Absolute zero is approximately -459.67°F.
The most common temperature conversions you are likely to perform involve changing a Fahrenheit reading to Celsius, or vice versa. Formulas have been developed for this purpose. Let F be the temperature in °F, and let C be the temperature in °C. Then, if you need to convert from °F to °C, use this formula:
F = 1.8C +32
If you need to convert a reading from °C to °F, use this formula:
C = 5/9(F - 32)
While the constants in these equations are expressed only to one or two significant figures (1.8, 5/9, and 32), they can be considered mathematically exact for calculation purposes.
Figure 1 is a nomograph you can use for approximate temperature conversions in the range from -50°C to +150°C.
When you hear someone say that the temperature at the core of a star is 30 million °F, the Rankine reading is about the same, but the Celsius and Kelvin readings are only about 5/9 as great.
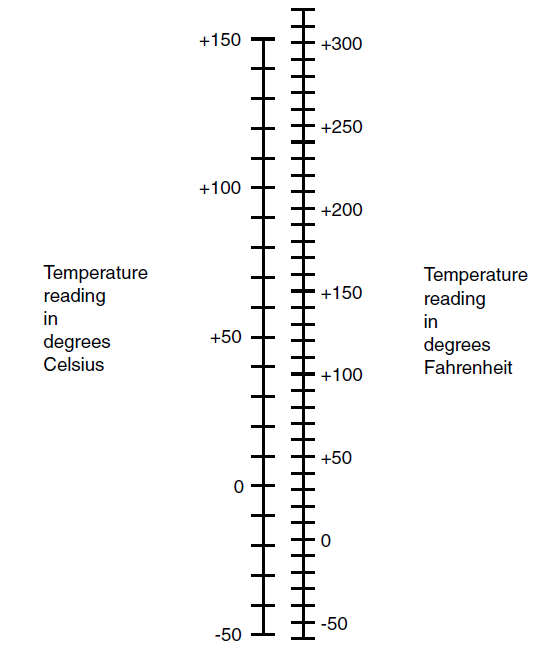
Fig. 1. This nomograph can be used for approximate conversions between temperatures in °F and °C.
 الاكثر قراءة في الديناميكا الحرارية
الاكثر قراءة في الديناميكا الحرارية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















