


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 31-10-2019
Date: 23-10-2019
Date: 28-7-2019
|
Epoxides may be cleaved by aqueous acid to give glycols that are often diastereomeric with those prepared by the syn-hydroxylation reaction described above. Proton transfer from the acid catalyst generates the conjugate acid of the epoxide, which is attacked by nucleophiles such as water in the same way that the cyclic bromonium ion described above undergoes reaction. The result is anti-hydroxylation of the double bond, in contrast to the syn-stereoselectivity of the earlier method. In the following equation this procedure is illustrated for a cis-disubstituted epoxide, which, of course, could be prepared from the corresponding cis-alkene. This hydration of an epoxide does not change the oxidation state of any atoms or groups.
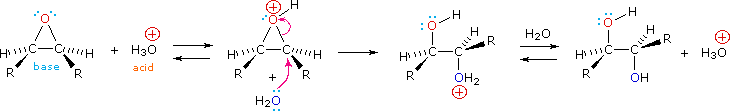
Osmium tetroxide oxidizes alkenes to give glycols through syn addition. A glycol, also known as a vicinal diol, is a compound with two -OH groups on adjacent carbons.
The reaction with OsO4 is a concerted process that has a cyclic intermediate and no rearrangements. Vicinal syn dihydroxylation complements the epoxide-hydrolysis sequence which constitutes an anti dihydroxylation of an alkene. When an alkene reacts with osmium tetroxide, stereocenters can form in the glycol product. Cis alkenes give meso products and trans alkenes give racemic mixtures.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ضمن مؤتمر ذاكرة الألم في العراق ورقة بحثية تتناول الأهداف والاستراتيجيات التي يعتمدها كرسي اليونسكو لتطوير دراسات حوار الأديان
|
|
|