


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 28-8-2018
Date: 3-8-2019
Date: 11-9-2018
|
In the term SN2, the S stands for substitution, the N stands for nucleophilic, and the number two stands for bimolecular, meaning there are two molecules involved in the rate determining step. The rate of bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions depends on the concentration of both the haloalkane and the nucleophile. To understand how the rate depends on the concentrations of both the haloalkane and the nucleophile, let us look at the following example. The hydroxide ion is the nucleophile and methyl iodide is the haloalkane.
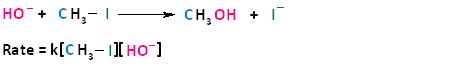
If we were to double the concentration of either the haloalkane or the nucleophile, we can see that the rate of the reaction would proceed twice as fast as the initial rate.
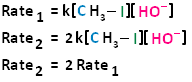
If we were to double the concentration of both the haloalkane and the nucleophile, we can see that the rate of the reaction would proceed four times as fast as the initial rate.
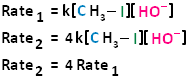
The bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction follows second-order kinetics; that is, the rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of two first-order reactants. In the case of bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, these two reactants are the haloalkane and the nucleophile.



|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أكبر محطة للطاقة الكهرومائية في بريطانيا تستعد للانطلاق
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أصواتٌ قرآنية واعدة .. أكثر من 80 برعماً يشارك في المحفل القرآني الرمضاني بالصحن الحيدري الشريف
|
|
|