


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 15-1-2020
Date: 22-11-2019
Date: 1-12-2019
|
In a tertiary (3°) halogenoalkane, the carbon atom holding the halogen is attached directly to three alkyl groups, which may be any combination of same or different. Examples:
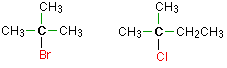
The Learning Objective is to name halogenated hydrocarbons given formulas and write formulas for these compounds given names.
Many organic compounds are closely related to the alkanes. As we noted in Section 12.7, alkanes react with halogens to produce halogenated hydrocarbons, the simplest of which have a single halogen atom substituted for a hydrogen atom of the alkane. Even more closely related are the cycloalkanes, compounds in which the carbon atoms are joined in a ring, or cyclic fashion.
The reactions of alkanes with halogens produce halogenated hydrocarbons, compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon have been replaced by halogen atoms:

The replacement of only one hydrogen atom gives an alkyl halide (or haloalkane). The common names of alkyl halides consist of two parts: the name of the alkyl group plus the stem of the name of the halogen, with the ending -ide. The IUPAC system uses the name of the parent alkane with a prefix indicating the halogen substituents, preceded by number indicating the substituent’s location. The prefixes are fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, and iodo-. Thus CH3CH2Cl has the common name ethyl chloride and the IUPAC name chloroethane. Alkyl halides with simple alkyl groups (one to four carbon atoms) are often called by common names. Those with a larger number of carbon atoms are usually given IUPAC names.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|