
 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 3-1-2017
Date: 22-3-2017
Date: 3-1-2017
|
The VSEPR model can be used to predict the structure of somewhat more complex molecules with no single central atom by treating them as linked AXmEn fragments. We will demonstrate with methyl isocyanate (CH3–N=C=O), a volatile and highly toxic molecule that is used to produce the pesticide Sevin. In 1984, large quantities of Sevin were accidentally released in Bhopal, India, when water leaked into storage tanks. The resulting highly exothermic reaction caused a rapid increase in pressure that ruptured the tanks, releasing large amounts of methyl isocyanate that killed approximately 3800 people and wholly or partially disabled about 50,000 others. In addition, there was significant damage to livestock and crops.
We can treat methyl isocyanate as linked AXmEn fragments beginning with the carbon atom at the left, which is connected to three H atoms and one N atom by single bonds. The four bonds around carbon mean that it must be surrounded by four bonding electron pairs in a configuration similar to AX4. We can therefore predict the CH3–N portion of the molecule to be roughly tetrahedral, similar to methane:
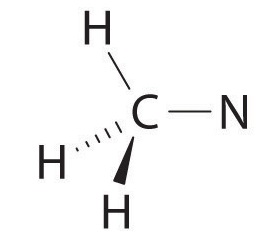
The nitrogen atom is connected to one carbon by a single bond and to the other carbon by a double bond, producing a total of three bonds, C–N=C. For nitrogen to have an octet of electrons, it must also have a lone pair:
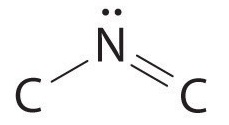
Because multiple bonds are not shown in the VSEPR model, the nitrogen is effectively surrounded by three electron pairs. Thus according to the VSEPR model, the C–N=C fragment should be bent with an angle less than 120°.
The carbon in the –N=C=O fragment is doubly bonded to both nitrogen and oxygen, which in the VSEPR model gives carbon a total of two electron pairs. The N=C=O angle should therefore be 180°, or linear. The three fragments combine to give the following structure:
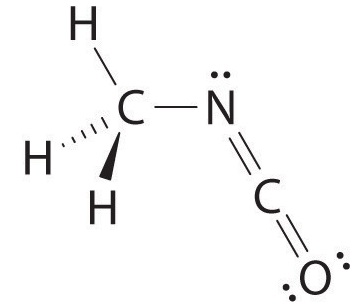
We predict that all four nonhydrogen atoms lie in a single plane, with a C–N–C angle of approximately 120°. The experimentally determined structure of methyl isocyanate confirms our prediction (Figure 1.1).
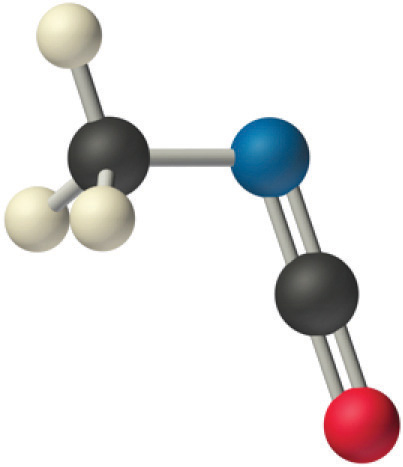
Figure 1.1 : The Experimentally Determined Structure of Methyl Isocyanate
Certain patterns are seen in the structures of moderately complex molecules. For example, carbon atoms with four bonds (such as the carbon on the left in methyl isocyanate) are generally tetrahedral. Similarly, the carbon atom on the right has two double bonds that are similar to those in CO2, so its geometry, like that of CO2, is linear. Recognizing similarities to simpler molecules will help you predict the molecular geometries of more complex molecules.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مجلةٌ عالميةٌ تنشر تفاصيل مشروع ملف تفويض المؤلِّفين العراقيين لحفظ التراث الفكري
|
|
|