


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 14-10-2019
Date: 10-5-2017
Date: 9-10-2020
|
Organic Acids
Organic acids are characterized by the presence of a positively polarized hydrogen atom (blue in electrostatic potential maps) and are of two main kinds: acids such as methanol and acetic acid that contain a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative oxygen atom (O-H) and those such as acetone that contain a hydrogen atom bonded to a carbon atom next to a C=O bond (O=C-C-H).
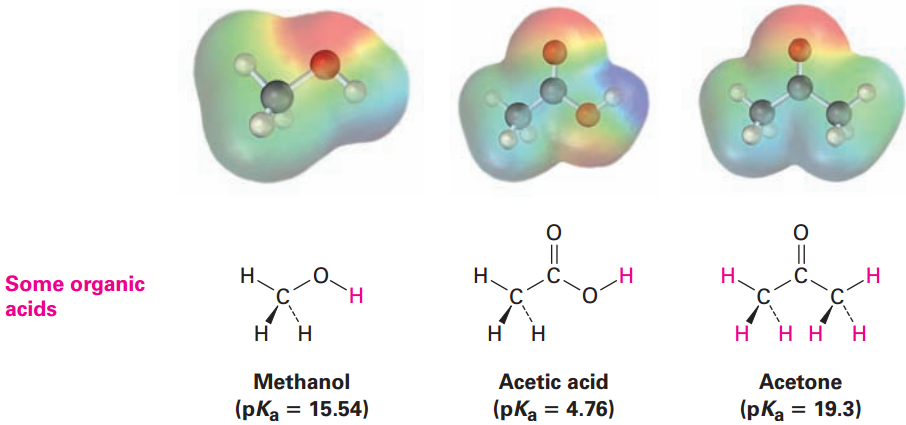
Methanol contains an O-H bond and is a weak acid, while acetic acid also contains an O-H bond and is a somewhat stronger acid. In both cases, acidity is due to the fact that the conjugate base resulting from loss of H+ is stabilized by having its negative charge on a strongly electronegative oxygen atom. In addition, the conjugate base of acetic acid is stabilized by resonance.
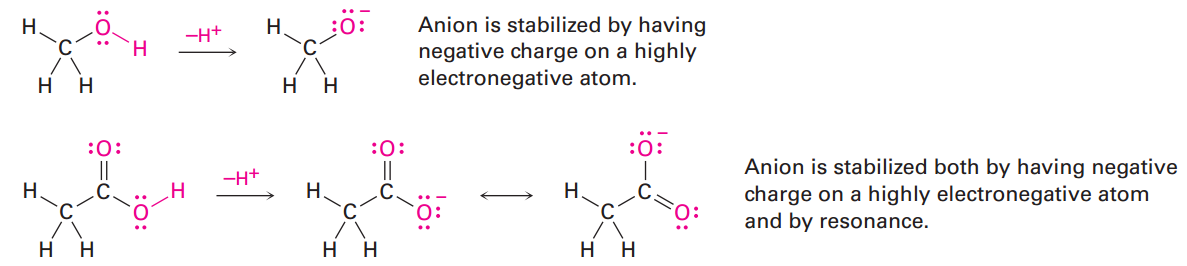
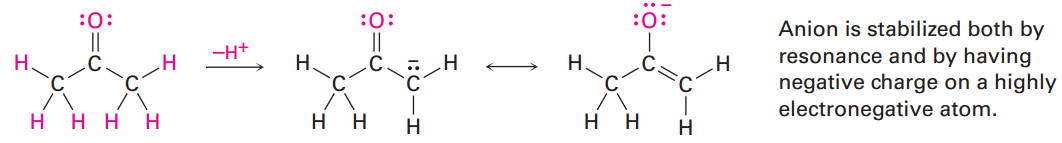
The acidity of acetone and other compounds with C=O bonds is due to the fact that the conjugate base resulting from loss of H+ is stabilized by resonance. In addition, one of the resonance forms stabilizes the negative charge by placing it on an electronegative oxygen atom.
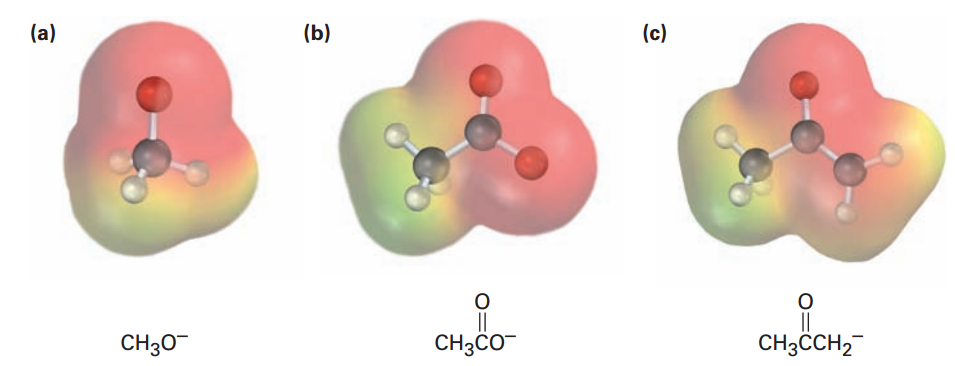
Electrostatic potential maps of the conjugate bases from methanol, acetic acid, and acetone are shown in FIGURE below As you might expect, all three show a substantial amount of negative charge (red) on oxygen.



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم التربية والتعليم يكرّم الطلبة الأوائل في المراحل المنتهية
|
|
|