
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء والفلسفة

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Physical Meaning of the Wave Function
المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
الجزء والصفحة:
p 32
13-5-2017
3925
Physical Meaning of the Wave Function
We are ultimately trying to use the wave function Ψ(x, t) to describe the behavior of an electron in a crystal. The function Ψ (x, t) is a wave function. so it is reasonable to ask what the relation is between the function and the electron. The total wave function is the product of the position-dependent, or time-independent, function and the time-dependent function.
 (1)
(1)
Since the total wave function Ψ(x, t) is a complex function. it cannot by itself represent a real physical quantity. Max Born postulated in 1926 that the function |Ψ(x, t)|2 dx is the probability of finding the particle between x and x + dx at a given time, or that |Ψ(x, t)|2 is a probability density function. We have that
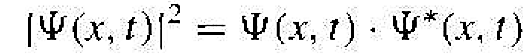 (2)
(2)
where Ψ*(x, t) is the complex conjugate function. Therefore

Then the product of the total wave function and its complex conjugate is given by
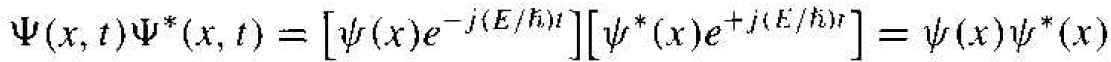 (3)
(3)
Therefore, we have that
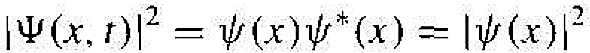 (4)
(4)
is the probability density function and is independent of time. One major difference between classical and quantum mechanics is that in classical mechanics, the position of a particle or body can be determined precisely, whereas in quantum mechanics, the position of a particle is found in terms of a probability. We will determine the probability density function for several examples, and, since this property is independent of time. we will, in general, only be concerned with the time-independent wave function.
 الاكثر قراءة في ميكانيكا الكم
الاكثر قراءة في ميكانيكا الكم
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















