
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
n = 2 Hydrogen with Electric and Magnetic Fields
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 69
19-8-2016
1479
n = 2 Hydrogen with Electric and Magnetic Fields
Consider an electron in the n = 2 state of the hydrogen atom. We ignore relativistic corrections, so the 2s and 2p states are initially degenerate. Then we impose two simultaneous perturbations: an electric field E in the x-direction 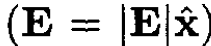 and a magnetic field B, which is given by the vector potential A = (B/2)(-y, x, 0). Ignore the magnetic moment of the electron. Calculate how the n = 0 states are altered by these simultaneous perturbations.
and a magnetic field B, which is given by the vector potential A = (B/2)(-y, x, 0). Ignore the magnetic moment of the electron. Calculate how the n = 0 states are altered by these simultaneous perturbations.
SOLUTION
The four orbital states: the s-state is |00⟩ and the three p-orbitals are |1 -1⟩, |10⟩, |11⟩. Here again, spin is not affected by this perturbation. We must evaluate the 10 different matrix elements ⟨LM|V(z)|L'M'⟩ which occur in the symmetric 4 × 4 matrix.
One interaction potential is V = -e|E|x. One can use parity and other group theory arguments to show that the only nonzero matrix elements are
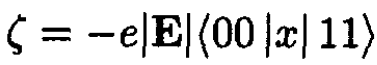 (1)
(1)
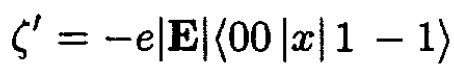 (2)
(2)
One can show that ζ and ζ' are equal to within a phase factor. We ignore this phase factor and call them equal. The evaluation of this integral was demonstrated in the previous solution. The result here is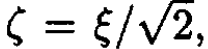 compared to the one in the previous problem.
compared to the one in the previous problem.
To first order in the magnetic field, the interaction is given by
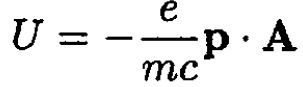 (3)
(3)
In spherical coordinates the three unit vectors for direction are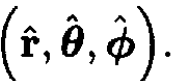
In these units the vector potential can be written as 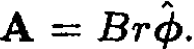 Similarly, the momentum operator in this direction is
Similarly, the momentum operator in this direction is
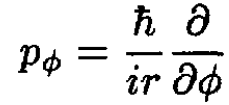 (4)
(4)
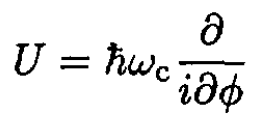 (5)
(5)
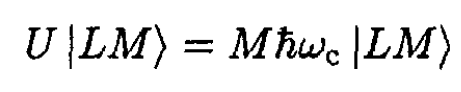 (6)
(6)
where the cyclotron frequency is ωc = eB/mc. The magnetic field is a diagonal perturbation in the basis |LM⟩.
Now the state|10⟩ has no matrix elements for these interactions and is unchanged by these interactions to lowest order. So we must diagonalize the 3 × 3 interaction matrix for the three states |00⟩, |11⟩, |1 – 1⟩:
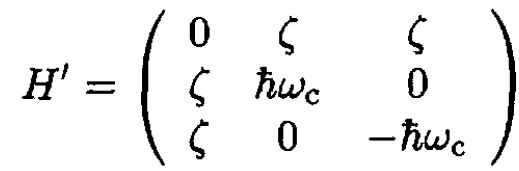 (7)
(7)
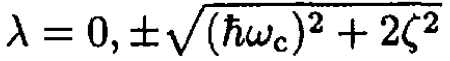 (8)
(8)
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















