
Harmonic Oscillator in Field
 المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
 المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
 الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 70
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 70
 18-8-2016
18-8-2016
 1471
1471
Harmonic Oscillator in Field
A particle of mass m and charge e moves in one dimension. It is attached to a spring of constant k and is initially in the ground state (n = 0) of the harmonic oscillator. An electric field E is switched on during the interval 0 < t < τ, where τ is a constant.
a) What is the probability of the particle ending up in the n = 1 state?
b) What is the probability of the particle ending up in the n = 2 state?
SOLUTION
Now we label the eigenstates with the index n for the harmonic oscillator state of energy En = hω(n + 1/2) and write the equation satisfied by the time-dependent amplitudes an(t),
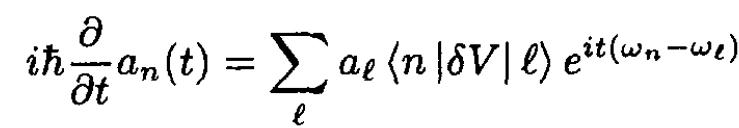 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
We need to evaluate the matrix element ⟨n|x|m⟩ of x between the states |n⟩ and |m⟩ of the harmonic oscillator. It is only nonzero if m = n ±1. In terms of raising and lowering operators,
 (3)
(3)
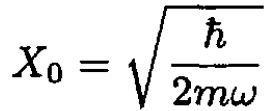 (4)
(4)
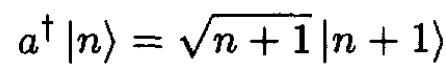 (5)
(5)
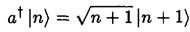 (6)
(6)
a) If the initial state is n = 0 at t = 0, then the amplitude of the n = 1 state for (t < τ) is given by
 (7)
(7)
 (8)
(8)
The last equation is the probability of ending in the state n = 1 if the initial state is n = 0. This expression is valid as long as it is less than 1 or if 2e|E|X0 < hω.
b) The n = 2 state cannot be reached by a single transition from n = 0 since the matrix element ⟨2|x|0⟩ = 0. However, n = 2 can be reached by a two-step process. It can be reached from n = 1, and n = 1 is excited from n = 0. The matrix element is so we have that
so we have that
 (9)
(9)
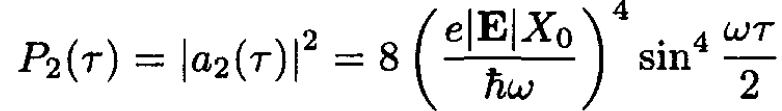 (10)
(10)
Note that P2 = P12/2!. Similarly, one can show that Pn = P1n/n! However, the total probability, when summed over all transitions, cannot exceed 1. Therefore, we define a normalized probability 
 (11)
(11)
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


