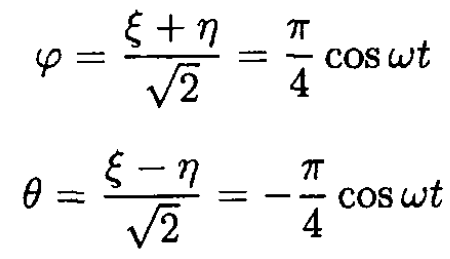تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Rotating Hollow Hoop
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 30
1-8-2016
1217
Rotating Hollow Hoop
A thin hollow cylindrical pipe is bent to form a hollow circular ring of mass m and radius R. The ring is attached by means of massless spokes to a vertical axis, around which it can rotate without friction in a horizontal plane. Inside the ring, a point mass P of mass m is free to move without friction, but is connected to a point H of the ring by a massless spring which exerts a force kΔs, where Δs is the length of the arc HP (see Figure 1.1). Take as variables the angles θ and φ of CH and CP with the x axis.
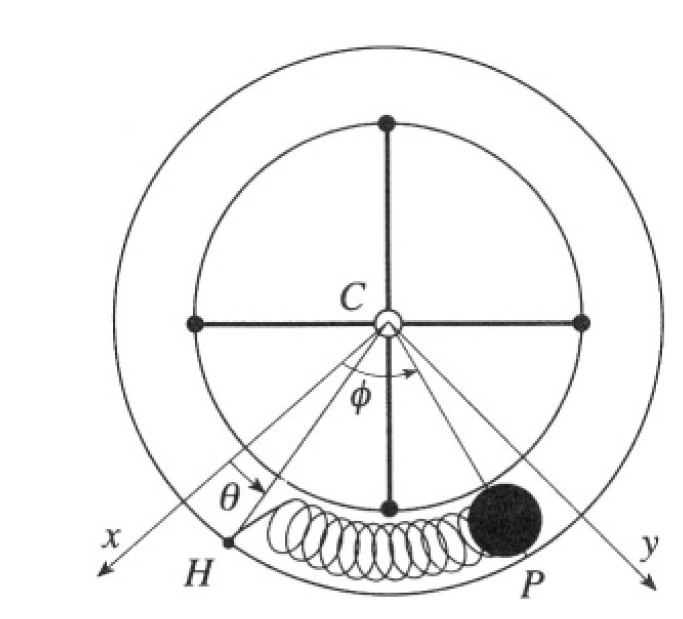
Figure 1.1
a) Write the Lagrangian and the Hamiltonian, and rewrite them in terms of the variables

b) Find an integral of motion other than the energy, and show that its Poisson bracket with H is zero.
c) Integrate the equations of motion with these initial conditions at t = 0:
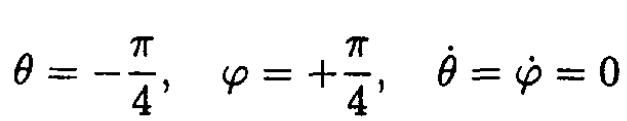
SOLUTION
The Lagrangian for the system shown in Figure 1.2 can be written in
the form
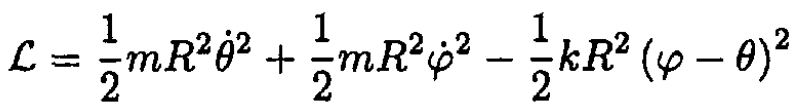
The generalized momenta are

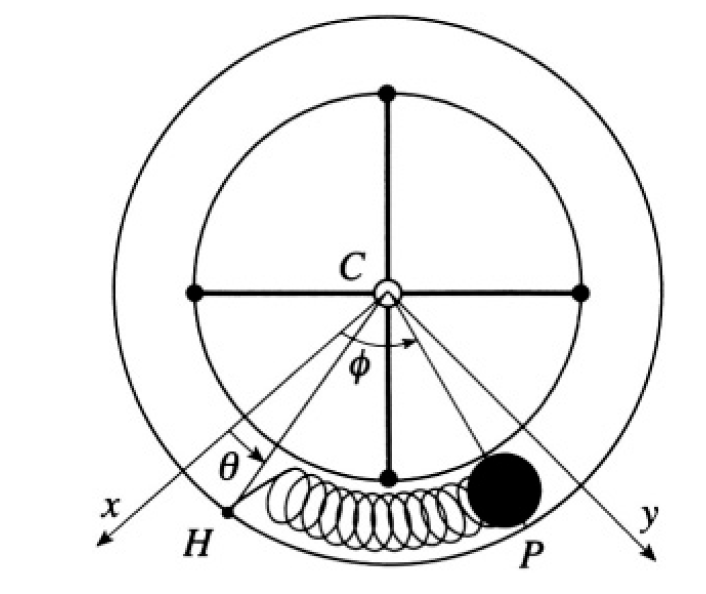
Figure 1.2
The Hamiltonian is
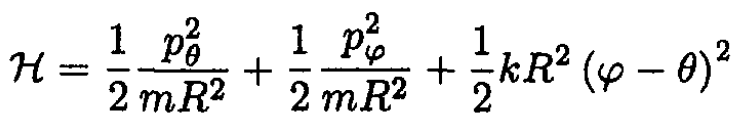
Changing the variables gives
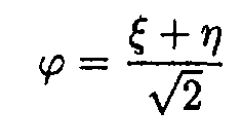 (1)
(1)
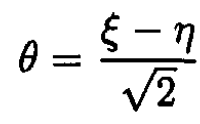 (2)
(2)
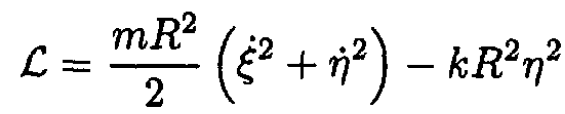 (3)
(3)
Again, the generalized momenta are
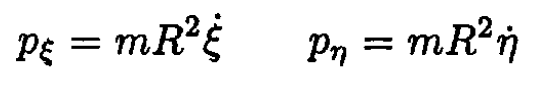
The Hamiltonian is
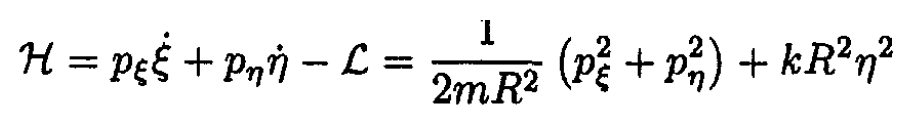
b) Since  we have
we have

The Poisson bracket of pζ with H is
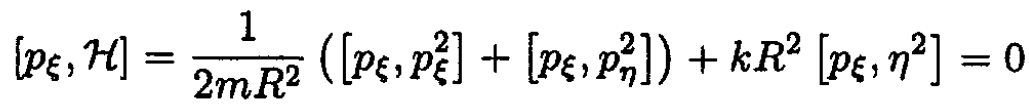
So, pζ is indeed the integral of motion since its Poisson bracket with H is equal to zero.
c) From (3), the equations of motion are
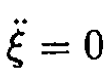 (4)
(4)
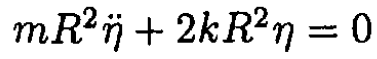 (5)
(5)
From (4) and (5) we obtain
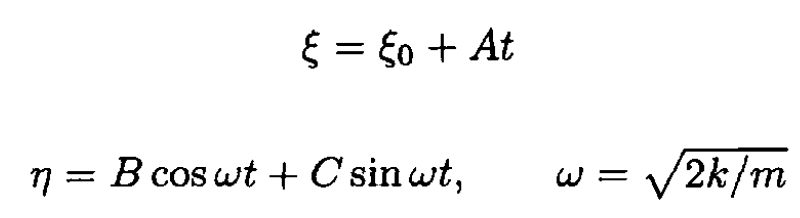
Using the initial conditions for (1) and (2) we have
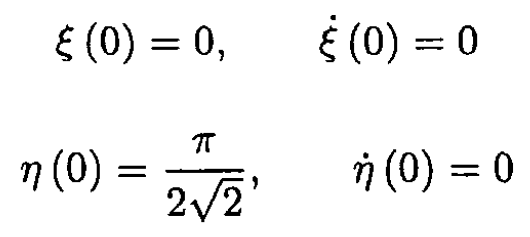
So
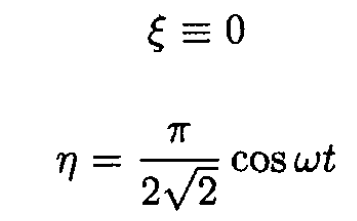
and finally