

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
White pigments
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
ص643-644
2025-10-13
45
White pigments
Key point: Titanium dioxide is used almost universally as a white pigment. White inorganic materials can also be classified as pigments and vast quantities of these compounds are synthesized for applications such as the production of white plastics and paints. Important commercial compounds of this class that have been used extensively historically are TiO2, ZnO, and ZnS, lead (II) carbonate, and lithopone (a mixture of ZnO and BaSO4); note that none of the metals in these materials has an incomplete d-electron shell that might otherwise induce colour through d-d transitions. Titanium dioxide, TiO2, in either its rutile or anatase forms (Fig. 24.66), is produced from titanium ores, often ilmenite, FeTiO3, by the sulfate process (which involves dissolution in concentrated H2SO4 and subsequent precipitation through hydrolysis) or the chloride process (which is based on the reaction of mixed complex titanium oxides with chlorine to produce TiCl4, which is then combusted with oxygen at over 1000ºC). These routes produce very high quality TiO2 free from impurities (which is essential for a bright white pigment) of controlled particle size. The desirable qualities of TiO2 as a white pigment derive from its excellent light scattering power, which in turn is a result of its high refractive index (nr2.70), the ability to produce very pure materials of a desired particle size, and its good light-fastness and weather resistance. Uses of titanium dioxide, which nowadays dominates the white pigment market, include paints, coatings, and printing ink (where it is often used in combination with coloured pigments to increase their brightness and hiding power), plastics, fibres, paper, white cements, and even foodstuffs (where it can be added to icing sugar, sweets, and flour to improve their brightness).
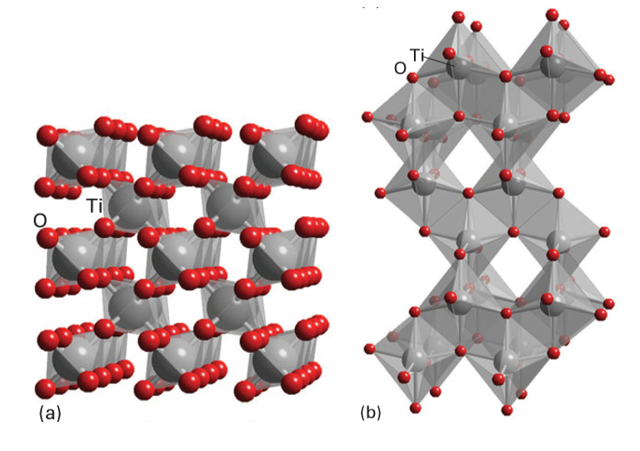
Figure 24.66 TiO2 exists as several polymorphs that can be described in terms of linked TiO6 octahedra, including the (a) rutile and (b) anatase forms.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















