


 7:57:24
7:57:24  2026-02-15
2026-02-15  50
50
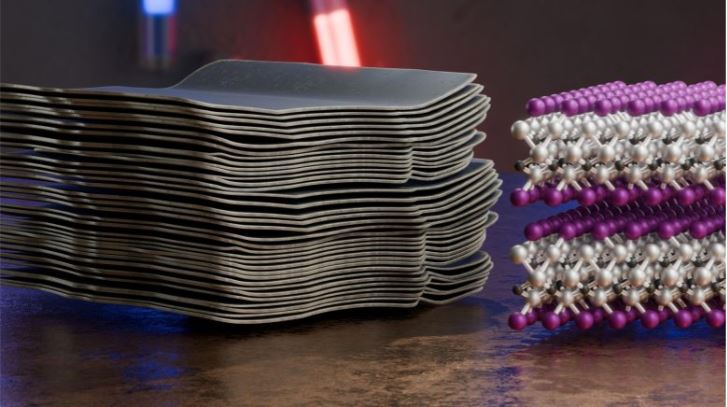

MXenes are an emerging class of two-dimensional materials whose properties depend sensitively on the atoms bound to their surfaces. A new synthesis approach now allows researchers to control these surface terminations with unprecedented precision.
First identified in 2011, MXenes are a fast-expanding family of ultra-thin inorganic materials only a few atoms thick. Their structure consists of stacked layers of transition metals bonded with carbon or nitrogen, while additional atoms attach to the exposed outer surfaces. These surface atoms are essential because they largely determine how the material behaves. “
“They strongly influence how electrons move through the material, how stable it is, and how it interacts with light, heat, and chemical environments,” explains Dr. Mahdi Ghorbani-Asl from the Institute of Ion Beam Physics and Materials Research at HZDR.
For years, MXenes have mainly been created through chemical etching processes. While effective, these techniques leave behind a patchwork of different surface atoms, commonly oxygen, fluorine, or chlorine, arranged in a disordered way. “This atomic disorder limits performance because it traps and scatters electrons, much like potholes slowing traffic on a highway,” describes Dr. Dongqi Li from TU Dresden.
The newly developed GLS technique takes a different approach by eliminating aggressive chemicals. Instead, it relies on solid precursor materials called MAX phases, combined with molten salts and iodine vapor, to form thin MXene sheets. This setup allows researchers to steer which halogen atoms, including chlorine, bromine, or iodine, bond to the surface. As a result, the MXenes produced this way have highly consistent and orderly surface structures, along with far fewer impurities.
Using the GLS method, the research team created MXenes from eight distinct MAX phases, demonstrating that the process works across a wide range of materials. The scientists also carried out density functional theory (DFT) calculations to better understand how different surface atoms affect both stability and electronic behavior.
“By combining theory with our experimental ability to precisely control surface terminations, we open a new path toward MXenes with improved stability and tailored functional properties,” concludes Ghorbani-Asl.
Outstanding conductivity from perfectly ordered surfaces
To showcase the significance of this advance, the researchers examined one of the most extensively studied MXenes, titanium carbide Ti₃C₂. When produced through standard chemical methods, Ti₃C₂ usually carries a mixture of chlorine and oxygen on its surface, which interferes with how electricity flows through the material. By contrast, Ti₃C₂Cl₂ made using the GLS process features only chlorine atoms, arranged in a precise and orderly pattern with no measurable contamination.
“The results were striking. The chlorine-terminated MXene variant showed a 160-fold increase in macroscopic conductivity and a 13-fold enhancement in terahertz conductivity compared with the same material made by traditional methods. In addition, a nearly fourfold increase in charge carrier mobility was observed, a key measure of how freely electrons move through a material,” Li summarizes.
These dramatic improvements can be traced directly to the cleaner surface chemistry. When chlorine atoms are evenly positioned across the MXene surface, electrons face fewer disruptions and can travel more efficiently. Computer-based quantum transport simulations confirmed this effect, showing that the orderly surfaces greatly reduce electron trapping and scattering, which explains the substantial gains seen in experiments.
Tailoring 2D materials for tomorrow’s technologies
Beyond electrical transport, the study shows that tuning the type of surface halogen also changes how MXenes absorb electromagnetic waves. This means the materials can be engineered for specific applications such as radar-absorbing coatings, electromagnetic shielding, and next-generation wireless components. For example, chlorine-terminated MXenes show strong absorption in the 14-18 GHz frequency range, while bromine- and iodine-terminated MXenes absorb in different frequency windows.
The method also provides a powerful platform for designing MXenes with tailored surface properties. By mixing different halide salts, the researchers produced MXenes with dual or even triple halogen terminations and precisely controlled ratios. This ability to “dial in” the surface composition offers a new toolkit for customizing MXenes for applications in electronics, catalysis, energy storage, photonics, and beyond.
Overall, the study represents a significant advance in MXene chemistry. For the first time, it demonstrates a gentle and broadly applicable synthesis route that yields highly ordered MXenes with precisely controlled surface terminations. According to the authors, the GLS method could accelerate the development of next-generation materials for flexible electronics, high-speed communication technologies, and advanced optoelectronic devices.
Reality Of Islam |
|

MXenes are
A newly dev

Get ready f

Researchers
 9:3:43
9:3:43
 2018-11-05
2018-11-05
10 benefits of Marriage in Islam
 7:5:22
7:5:22
 2019-04-08
2019-04-08
benefits of reciting surat yunus, hud &
 9:45:7
9:45:7
 2018-12-24
2018-12-24
advantages & disadvantages of divorce
 11:35:12
11:35:12
 2018-06-10
2018-06-10
 6:0:51
6:0:51
 2018-10-16
2018-10-16
 11:34:48
11:34:48
 2022-06-29
2022-06-29
 3:43:50
3:43:50
 2022-11-05
2022-11-05
 2:33:4
2:33:4
 2023-02-15
2023-02-15
 7:59:14
7:59:14
 2018-06-21
2018-06-21
 9:39:36
9:39:36
 2022-12-28
2022-12-28
 11:11:59
11:11:59
 2023-02-01
2023-02-01
 1:38:41
1:38:41
 2021-12-08
2021-12-08
 5:41:46
5:41:46
 2023-03-18
2023-03-18
| LATEST |