


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية | Epoxide ring-opening reactions - SN1 vs. SN2, regioselectivity, and stereoselectivity |
|
|
|
Read More
Date: 24-1-2020
Date: 12-7-2018
Date: 22-12-2016
|
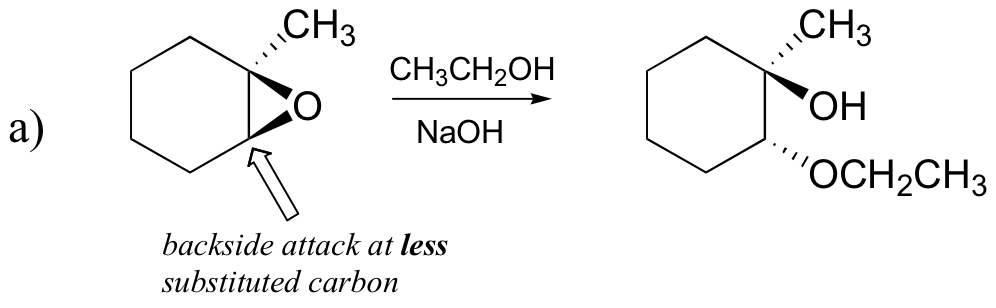
The nonenzymatic ring-opening reactions of epoxides provide a nice overview of many of the concepts we have seen already in this chapter. Ring-opening reactions can proceed by either SN2 or SN1 mechanisms, depending on the nature of the epoxide and on the reaction conditions. If the epoxide is asymmetric, the structure of the product will vary according to which mechanism dominates. When an asymmetric epoxide undergoes solvolysis in basic methanol, ring-opening occurs by an SN2 mechanism, and the less substituted carbon is the site of nucleophilic attack, leading to what we will refer to as product B:
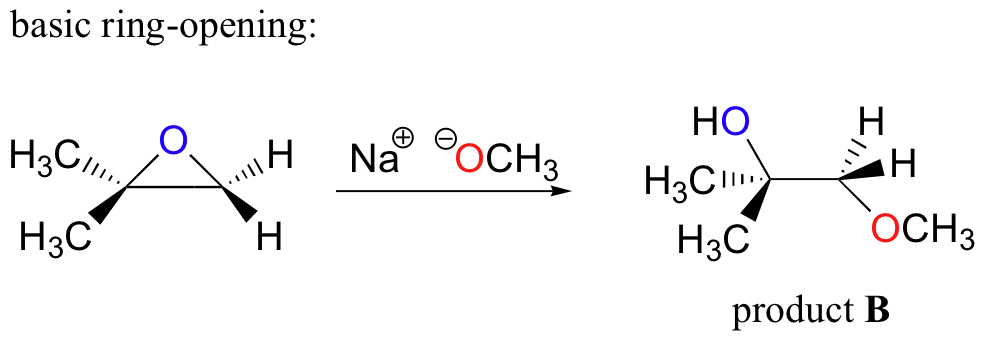
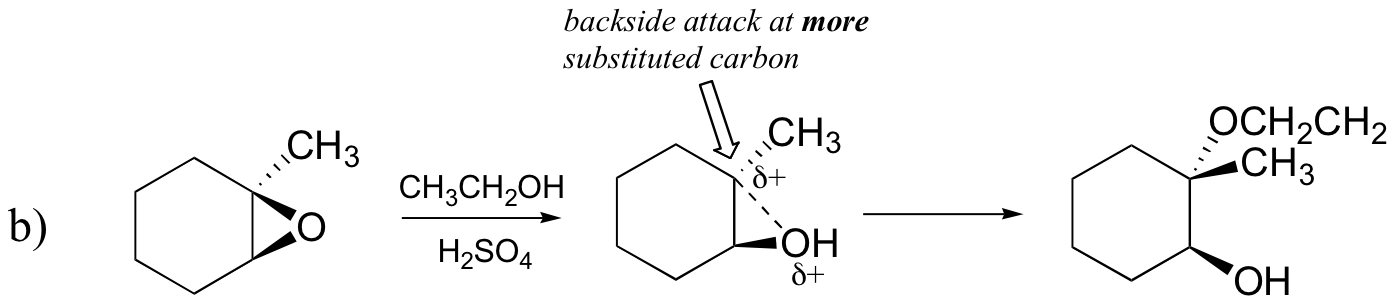
Conversely, when solvolysis occurs in acidic methanol, the reaction occurs by a mechanism with substantial SN1 character, and the more substituted carbon is the site of attack. As a result, product A predominates.

These are both good examples of regioselective reactions. In a regioselective reaction, two (or more) different constitutional isomers are possible as products, but one is formed preferentially (or sometimes exclusively).
Let us examine the basic, SN2 case first. The leaving group is an alkoxide anion, because there is no acid available to protonate the oxygen prior to ring opening. An alkoxide is a poor leaving group, and thus the ring is unlikely to open without a 'push' from the nucleophile.
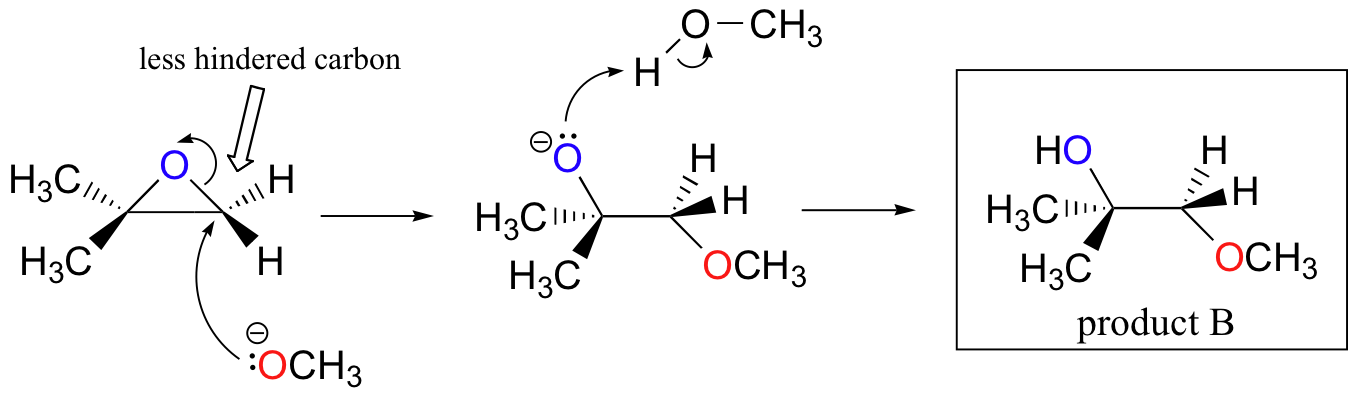
The nucleophile itself is potent: a deprotonated, negatively charged methoxide ion. When a nucleophilic substitution reaction involves a poor leaving group and a powerful nucleophile, it is very likely to proceed by an SN2 mechanism.
What about the electrophile? There are two electrophilic carbons in the epoxide, but the best target for the nucleophile in an SN2 reaction is the carbon that is least hindered. This accounts for the observed regiochemical outcome. Like in other SN2 reactions, nucleophilic attack takes place from the backside, resulting in inversion at the electrophilic carbon.
Probably the best way to depict the acid-catalyzed epoxide ring-opening reaction is as a hybrid, or cross, between an SN2 and SN1 mechanism. First, the oxygen is protonated, creating a good leaving group (step 1 below) . Then the carbon-oxygen bond begins to break (step 2) and positive charge begins to build up on the more substituted carbon (recall the discussion from section 8.4B about carbocation stability).

Unlike in an SN1 reaction, the nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbon (step 3) before a complete carbocation intermediate has a chance to form.
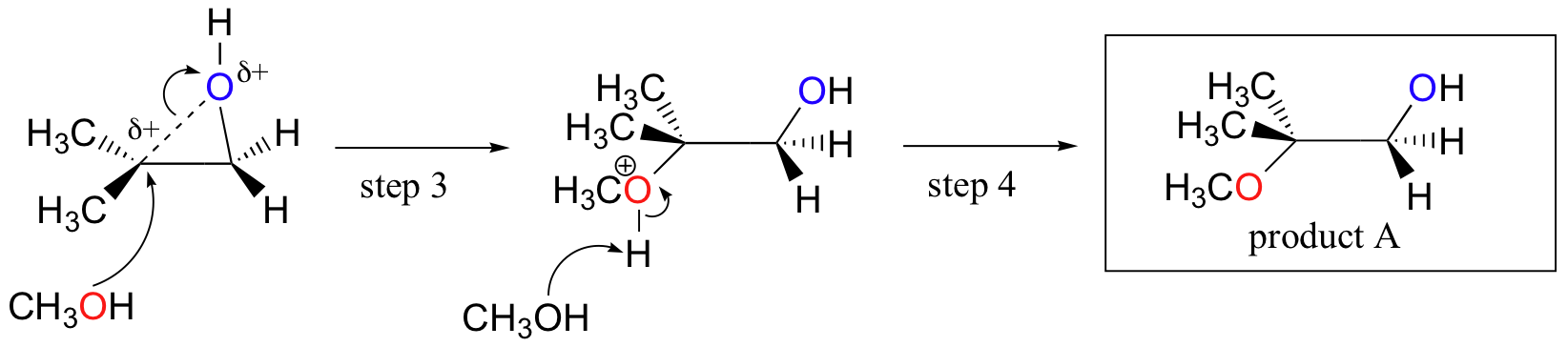
Attack takes place preferentially from the backside (like in an SN2 reaction) because the carbon-oxygen bond is still to some degree in place, and the oxygen blocks attack from the front side. Notice, however, how the regiochemical outcome is different from the base-catalyzed reaction: in the acid-catalyzed process, the nucleophile attacks the more substituted carbon because it is this carbon that holds a greater degree of positive charge.
Example 1
Predict the major product(s) of the ring opening reaction that occurs when the epoxide shown below is treated with:
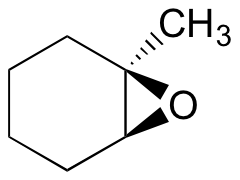
Hint: be sure to consider both regiochemistry and stereochemistry!
Answer:



|
|
|
|
حمية العقل.. نظام صحي لإطالة شباب دماغك
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
إيرباص تكشف عن نموذج تجريبي من نصف طائرة ونصف هليكوبتر
|
|
|
|
|
|
بمشاركة 60 ألف طالب.. المجمع العلمي يستعدّ لإطلاق مشروع الدورات القرآنية الصيفية
|
|
|
|
صدور العدد الـ 33 من مجلة (الاستغراب) المحكمة
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي ينظّم ورشة تطويرية لأساتذة الدورات القرآنية في كربلاء
|
|
|
|
شعبة التوجيه الديني النسوي تختتم دورتها الثانية لتعليم مناسك الحجّ
|