


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 5-3-2019
Date: 29-1-2018
Date: 25-6-2020
|
Relativistic effects of The group 13 elements
Among many generalizations about heavier elements are two that depend on quantum theory for explanation:
These observations can be accounted for (though often far from simply) if Einstein’s theory of relativity is combined with quantum mechanics, in which case they are attributed to relativistic effects. We focus here on chemical generalizations. According to the theory of relativity, the mass m of a particle increases from its rest mass m0 when its velocity v approaches the speed of light, c, and m is then given by the equation:
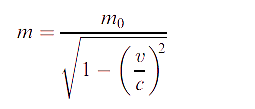
For a one-electron system, the Bohr model of the atom (which, despite its shortcomings, gives the correct value for the ionization energy) leads to the velocity of the electron being expressed by the equation:

the increase in m results in an approximately 20% contraction of the radius of the 1s (n = 1) orbital; this is called relativistic contraction. Other s orbitals are affected in a similar way and as a consequence, when Z is high, s orbitals have diminished overlap with orbitals of other atoms. A detailed treatment shows that p orbitals (which have a low electron density near to the nucleus) are less affected. On the other hand, d orbitals (which are more effectively screened from the nuclear charge by the contracted s and p orbitals) undergo a relativistic expansion; a similar argument applies to f orbitals.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|