


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 18-1-2016
Date: 29-3-2016
Date: 18-1-2016
|
α-ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONISTS
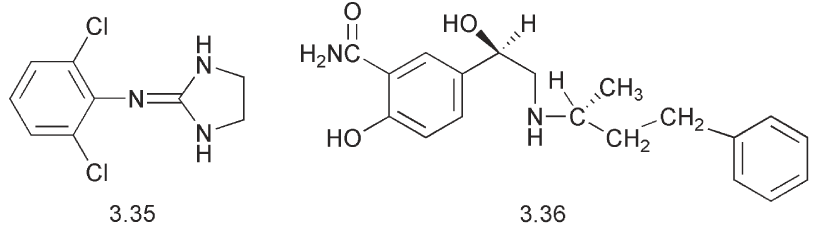
Clonidine 3.35 bears a formal resemblance to β-phenylethylamine. This compound and related imidazolines have attracted interest as antihypertensive agents to reduce blood pressure. They act as adrenergic agonists at α2-receptors. Whereas the α1-receptors are post-synaptic receptors, stimulation of which induces the adrenergic pharmacological effects, the α2-receptors are pre-synaptic receptors and binding to them leads to a regulation and an inhibition of the release of the neurotransmitter. Clonidine, while it is an adrenergic agonist, because it is selective for the α2-receptor it regulates the availability of noradrenalin and thus it exerts an anti-hypertensive effect. The chlorine atoms play an important steric role by twisting the imidazoline ring out of the plane of the aromatic ring. Calculations have been made on the optimum conformation of noradrenalin. The distances between the centre of the aromatic ring and the side chain nitrogen are comparable to the distances in clonidine.
An antagonist that has anti-hypertensive activity is labetalol 3.36. This compound has two asymmetric centres and hence there are four optical isomers. The RR enantiomer is the best for binding to and blocking the β-adrenergic receptor while the S isomer of the benzylic alcohol showed some activity as an antagonist of the α-receptors. These differences reveal the importance of discussing the biological activity of particular enantiomers.



|
|
|
|
"إنقاص الوزن".. مشروب تقليدي قد يتفوق على حقن "أوزيمبيك"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الصين تحقق اختراقا بطائرة مسيرة مزودة بالذكاء الاصطناعي
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ووفد من جامعة البصرة يبحثان سبل تعزيز التعاون المشترك
|
|
|