

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Heat, Energy, and Enthalpy
المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
المصدر:
College Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 42
1-7-2017
2082
Heat, Energy, and Enthalpy
Energy can be transferred to (or from) a chemical system from (or to) the surroundings in the form of heat q or work w. The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in the system's internal energy E is equal to the sum of the heat and work inputs (or outputs):
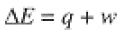 (1.1)
(1.1)
where DE = Efinal - Einitial. The first law of thermodynamics can be thought of as an extension of the mechanical law of conservation of energy to include heat. Notice that positive heat or work increases the energy of the system, negative heat or work decreases the energy. The internal energy change includes changes in the energies of atomic and molecular motion, changes in the energies of atomic and molecular interactions, and changes associated with a chemical reaction.
Heat energy flows to or from the surroundings when there is a difference in temperature, when a chemical reaction or change of state takes place, or when work is done on or by the system. Unlike P, V, T, and E, heat is not a function of the state of the system. We cannot speak of a system ''having heat"; q refers only to energy in transit.
Work is done on (or by) a chemical system when the system is compressed (or is expanded). Thus when V is constant, w = 0 and
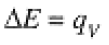 (1.2)
(1.2)
where the subscript reminds us that V is constant. When the pressure is constant, w = -P DV, q = ΔE - w, or qp = ΔE + P ΔV. Since E, P, and V are all variables associated with the state of the system, we can define a state function called the enthalpy,
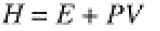 (1.3)
(1.3)
and, for a process occurring at constant pressure, the change in enthalpy is
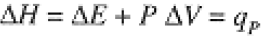 (1.4)
(1.4)
For most chemical processes, we can think of energy and enthalpy as nearly identical since heat transfer is usually much more important than work performed. However, since the work term can be significant, we must
maintain the distinction between E and H.
We will use the joule (J) to measure energy, enthalpy, and heat. Other energy units which may be encountered are listed in Table 1.1.
Table 1.1. Some Common Energy Units

 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحرارية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحرارية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















