
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Impurities in Solids
المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
الجزء والصفحة:
p 15
8-5-2017
1898
Impurities in Solids
Foreign atoms, or impurity atoms, may be present in a crystal lattice. Impurity atoms may be located at normal lattice sites, in which case they are called .substitutional impurities.
Impurity atoms may also be located between normal sites, in which case they are called interstitial impurities. Both these impurities are lattice defects and are schematically shown in Figure 1.1. Some impurities, such as oxygen in silicon, tend to he essentially inert; however, other impurities, such as gold or phosphorus in silicon, can drastically alter the electrical properties of the material.
By adding controlled amounts of particular impurity atoms, the electrical characteristics of a semiconductor material can be favorably altered. The technique of adding impurity atoms to a semiconductor material in order to change its conductivity is called duping. There are two general methods of doping: impurity diffusion and ion implantation.
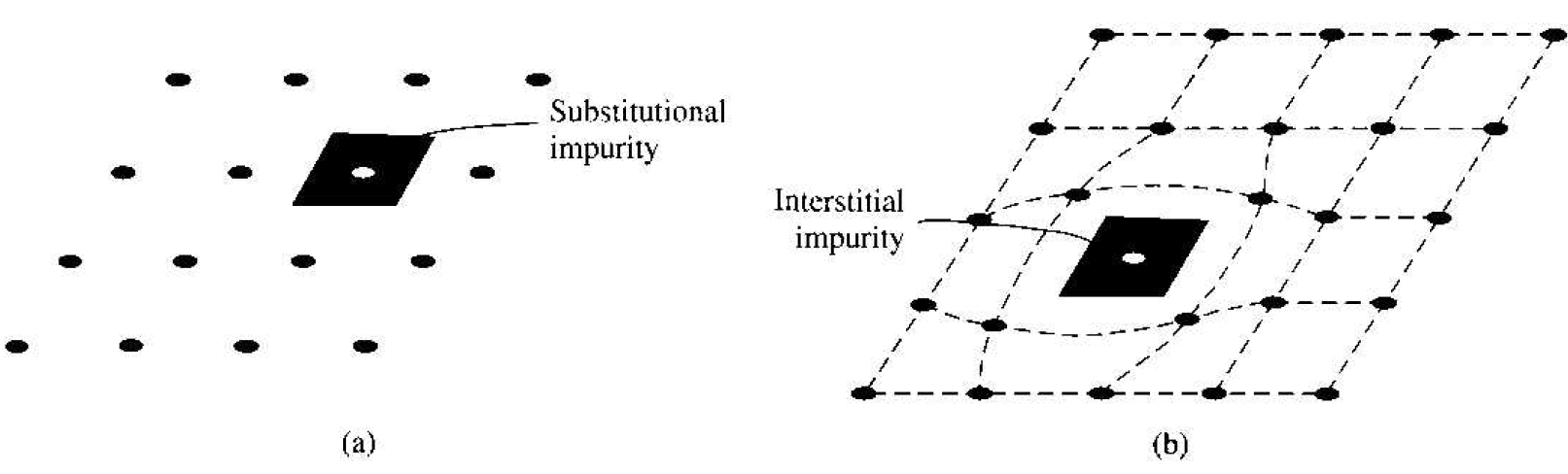
Figure 1.2 Two-dimensional representation of a single-crystal lattice showing (a) a substitutional impurity and (b) an intersitital impurity
The actual diffusion process depends to some extent on the material but, in general, impurity diffusion occurs when a semiconductor crystal is placed in a high temperature (≈ 1000o C) gaseous atmosphere containing the desired impurity atom. At this high temperature, many of the crystal atoms can randomly move in and out of their single-crystal lattice sites. Vacancies may he created by this random motion so that impurity atoms can move through the lattice by hopping from one vacancy to another. Impurity diffusion is the process by which impurity particles move from a region of high concentration near the surface, to a region of lower concentration within the crystal. When the temperature decreases, the impurity atoms become permanently frozen into the substitutional lattice sites. Diffusion of various impurities into selected regions of a semiconductor allows us to fabricate complex electronic circuits in a single semiconductor crystal.
Ion implantation generally takes place at a lower temperature than diffusion. A beam of impurity ions is accelerated to kinetic energies in the range of 50 keV or greater and then directed to the surface of the semiconductor. The high-energy impurity ions enter the crystal and come to rest at some average depth from the surface.
One advantage of ion implantation is that controlled numbers of impurity atoms can be introduced into specific regions of the crystal. A disadvantage of this technique is that the incident impurity atoms collide with the crystal atoms. causing lattice displacement damage. However, most of the lattice damage can he removed by thermal annealing, in which the temperature of the crystal is raised for a short time. Thermal annealing is a required step after implantation.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















