


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 12-3-2017
Date: 14-3-2017
Date: 14-3-2017
|

Names of Angles
As the Angle Increases, the Name Changes:
|
Type of Angle |
Description |
|
|
Acute Angle |
an angle that is less than 90° |
|
|
Right Angle |
an angle that is 90° exactly |
|
|
Obtuse Angle |
an angle that is greater than 90° but |
|
|
Straight Angle |
an angle that is 180° exactly |
|
|
Reflex Angle |
an angle that is greater than 180° |
|
In One Diagram This diagram might make it easier to remember: Also: Acute, Obtuse and Reflex are in alphabetical order. |
|
Be Careful What You Measure
|
|
|
|
This is an Obtuse Angle |
And this is a Reflex Angle |
|
|
|
|
But the lines are the same ... so when naming the angles make sure |
|
Positive and Negative Angles
When measuring from a line:
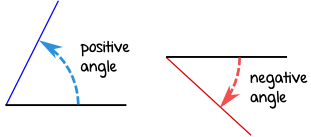
Example: −67°

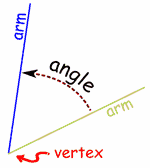
Parts of an Angle
The corner point of an angle is called the vertex
And the two straight sides are called arms
The angle is the amount of turn between each arm.
Labelling Angles
|
There are two main ways to label angles: 1. give the angle a name, usually a lower-case letter like a or b, or sometimes a Greek letter like α (alpha) or θ (theta) 2. or by the three letters on the shape that define the angle, with the middle letter being where the angle actually is (its vertex). Example angle "a" is "BAC", and angle "θ" is "BCD"
Acute |
|
An Acute Angle is less than 90°

This is an acute angle
All the angles below are acute angles:
Which Angle?
Remember to look carefully at which angle you are being asked to name:
The acute angle is the small angle which is less than 90°.
|
If you choose the larger angle you would |
|
|
|
The smaller angle is an Acute Angle, |
Right Angles
A right angle is an internal angle which is equal to 90°

This is a right angle
Note the special symbol like a box in the angle. If you see this, it is a right angle. The 90° is rarely written in. If you see the box in the corner, you are being told it is a right angle.
All the angles below are right angles:
A right angle can be in any orientation or rotation as long as the internal angle is 90°
Obtuse Angle
An Obtuse Angle is more than 90° but less than 180°
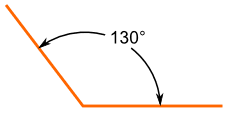
This is an obtuse angle !
All the angles below are obtuse angles:

Straight Angle
A straight angle is 180 degrees
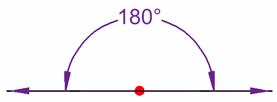
This is a straight angle
A straight angle changes the direction to point the opposite way.
Sometimes people say "You did a complete 180 on that!" ... meaning you completely changed your mind, idea or direction.
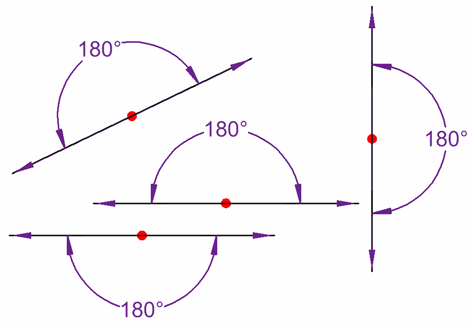
All the angles below are straight angles:
Reflex Angles
Different Angles have different names:
A Reflex Angle is more than 180° but less than 360°
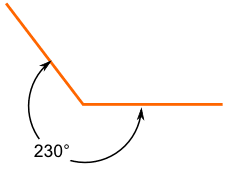
This is a reflex angle
All the angles below are reflex angles:
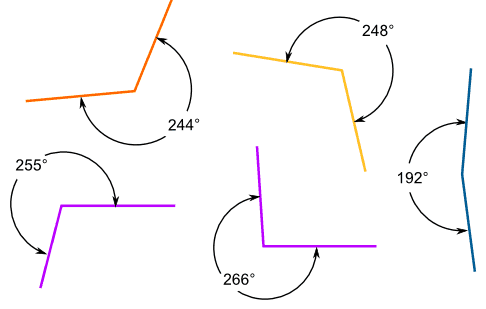
Which Angle?
Remember to look carefully at which angle you are being asked to name.
The reflex angle is the larger angle.
It is more than 180° but less than 360°
If you choose the smaller angle you might have an Acute Angle, or an Obtuse Angle instead:
|
|
|
|
|
The larger angle is a Reflex Angle, |
|
The larger angle is a Reflex Angle, |
Full Rotation
A full rotation is 360 degrees
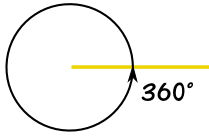
This is a "full rotation" or "revolution" or "complete turn" or "full circle"
Other ways of saying it:
|
This image of a protractor shows Also: Half a rotation is 180° Quarter of a rotation is 90° |
|
And a full rotation is also equal to 2π Radians, so here are some equivalent values:
|
Rotations |
Radians |
Degrees |
|
¼ |
π/2 |
90° |
|
½ |
π |
180° |
|
1 |
2π |
360° |
|
1½ |
3π |
540° |
|
2 |
4π |
720° |



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|